-
Product Name
Phospho-PRKACA-T197 pAb
- Documents
-
Description
Polyclonal antibody to Phospho-PRKACA-T197
-
Tested applications
WB
-
Species reactivity
Human, Mouse, Rat
-
Alternative names
PRKACA antibody; PKACA antibody; PPNAD4 antibody; cAMP-dependent protein kinase catalytic subunit alpha antibody
-
Isotype
Rabbit IgG
-
Preparation
Antigen: A synthetic phosphorylated peptide around T197 of human PRKACA (NP_002721.1).
-
Clonality
Polyclonal
-
Formulation
PBS with 0.02% sodium azide, 50% glycerol, pH7.3.
-
Storage instructions
Store at -20℃. Avoid freeze / thaw cycles.
-
Applications
WB 1:500 - 1:2000
-
Validations
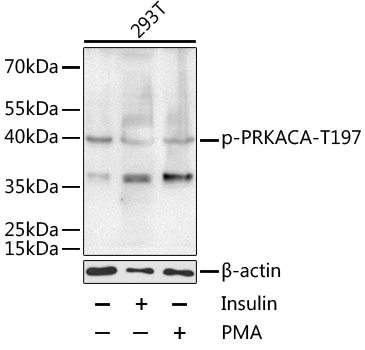
Western blot - Phospho-PRKACA-T197 pAb
Western blot analysis of extracts of 293T cells,using Phospho-PRKACA-T197 antibody at 1:1000 dilution. 293T cells were treated by Insulin (100nM) for 10 minutes or treated by PMA/TPA (200nM) for 30 minutes after serum-starvation overnight.Secondary antibody: HRP Goat Anti-Rabbit IgG (H+L) at 1:10000 dilution.Lysates/proteins: 25ug per lane.Blocking buffer: 3% BSA.
-
Background
Phosphorylates a large number of substrates in the cytoplasm and the nucleus. Regulates the abundance of compartmentalized pools of its regulatory subunits through phosphorylation of PJA2 which binds and ubiquitinates these subunits, leading to their subsequent proteolysis. Phosphorylates CDC25B, ABL1, NFKB1, CLDN3, PSMC5/RPT6, PJA2, RYR2, RORA and VASP. RORA is activated by phosphorylation. Required for glucose-mediated adipogenic differentiation increase and osteogenic differentiation inhibition from osteoblasts. Involved in the regulation of platelets in response to thrombin and collagen; maintains circulating platelets in a resting state by phosphorylating proteins in numerous platelet inhibitory pathways when in complex with NF-kappa-B (NFKB1 and NFKB2) and I-kappa-B-alpha (NFKBIA), but thrombin and collagen disrupt these complexes and free active PRKACA stimulates platelets and leads to platelet aggregation by phosphorylating VASP. Prevents the antiproliferative and anti-invasive effects of alpha-difluoromethylornithine in breast cancer cells when activated. RYR2 channel activity is potentiated by phosphorylation in presence of luminal Ca(2+), leading to reduced amplitude and increased frequency of store overload-induced Ca(2+) release (SOICR) characterized by an increased rate of Ca(2+) release and propagation velocity of spontaneous Ca(2+) waves, despite reduced wave amplitude and resting cytosolic Ca(2+). PSMC5/RPT6 activation by phosphorylation stimulates proteasome. Negatively regulates tight junctions (TJs) in ovarian cancer cells via CLDN3 phosphorylation. NFKB1 phosphorylation promotes NF-kappa-B p50-p50 DNA binding. Involved in embryonic development by down-regulating the Hedgehog (Hh) signaling pathway that determines embryo pattern formation and morphogenesis. Prevents meiosis resumption in prophase-arrested oocytes via CDC25B inactivation by phosphorylation. May also regulate rapid eye movement (REM) sleep in the pedunculopontine tegmental (PPT). Phosphorylates APOBEC3G and AICDA. Isoform 2 phosphorylates and activates ABL1 in sperm flagellum to promote spermatozoa capacitation. Phosphorylates HSF1; this phosphorylation promotes HSF1 nuclear localization and transcriptional activity upon heat shock.
Related Products / Services
Please note: All products are "FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY AND ARE NOT INTENDED FOR DIAGNOSTIC OR THERAPEUTIC USE"
