-
Product Name
PFKL antibody
- Documents
-
Description
PFKL Rabbit Polyclonal antibody. Positive IHC detected in human liver cancer tissue. Positive WB detected in HeLa cells. Observed molecular weight by Western-blot: 85 kDa
-
Tested applications
ELISA, IHC, WB
-
Species reactivity
Human,Mouse,Rat; other species not tested.
-
Alternative names
DKFZp686G1648 antibody; DKFZp686L2097 antibody; FLJ30173 antibody; FLJ40909 antibody; PFK B antibody; PFKL antibody; Phosphofructokinase 1 antibody; phosphofructokinase antibody; liver antibody; Phosphohexokinase antibody
-
Isotype
Rabbit IgG
-
Preparation
This antibody was obtained by immunization of PFKL recombinant protein (Accession Number: NM_002626). Purification method: Antigen affinity purified.
-
Clonality
Polyclonal
-
Formulation
PBS with 0.02% sodium azide and 50% glycerol pH 7.3.
-
Storage instructions
Store at -20℃. DO NOT ALIQUOT
-
Applications
Recommended Dilution:
WB: 1:200-1:2000
IHC: 1:20-1:200
-
Validations
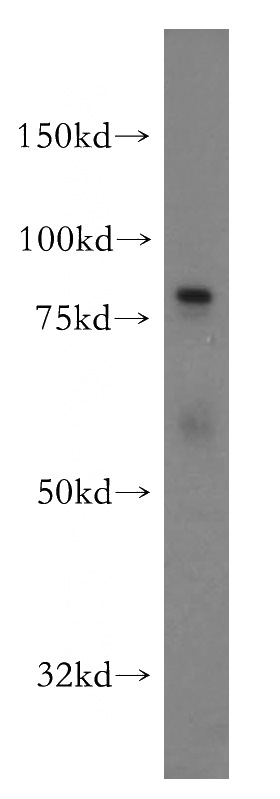
HeLa cells were subjected to SDS PAGE followed by western blot with Catalog No:113771(PFKL antibody) at dilution of 1:500
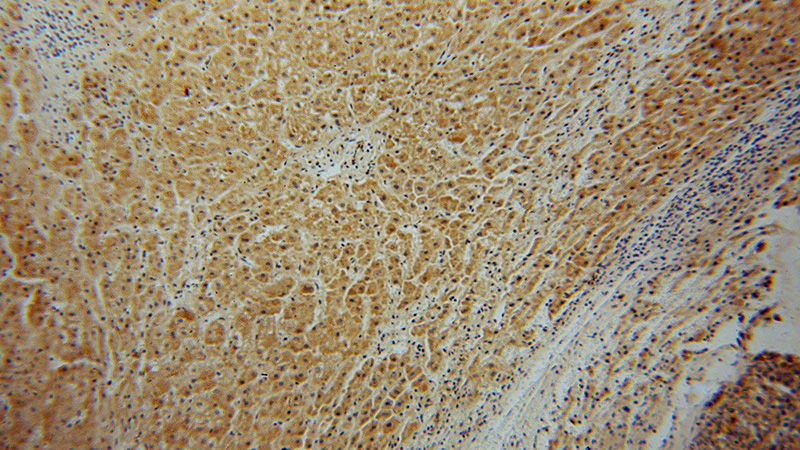
Immunohistochemical of paraffin-embedded human liver cancer using Catalog No:113771(PFKL antibody) at dilution of 1:50 (under 10x lens)
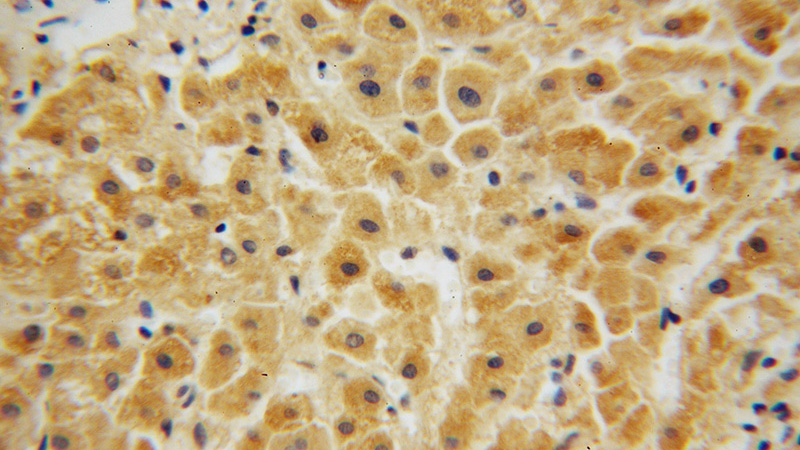
Immunohistochemical of paraffin-embedded human liver cancer using Catalog No:113771(PFKL antibody) at dilution of 1:50 (under 40x lens)
-
Background
PFKL(6-phosphofructokinase, liver type) is also named as PFK-B and belongs to the phosphofructokinase family. The PFKL gene encodes the liver isoform of phosphofructokinase (PFK)(ATP:D-fructose-6-phosphate-1-phosphotransferase).PFK catalyzes the irreversible conversion of fructose-6-phosphate to fructose-1,6-bisphosphate and is a key regulatory enzyme in glycolysis. In human beings,PFK exsits as a system of three of subunits: these are the muscle(PFKM), liver(PFKL), and platelet(PFKP) PFKs(PMID: 2139864). It has 2 isoforms produced by alternative splicing.
-
References
- Sun L, Song L, Wan Q. cMyc-mediated activation of serine biosynthesis pathway is critical for cancer progression under nutrient deprivation conditions. Cell research. 25(4):429-44. 2015.
Related Products / Services
Please note: All products are "FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY AND ARE NOT INTENDED FOR DIAGNOSTIC OR THERAPEUTIC USE"
