-
Product Name
PARN Polyclonal Antibody
- Documents
-
Description
Polyclonal antibody to PARN
-
Tested applications
WB, IF
-
Species reactivity
Human
-
Alternative names
PARN antibody; DAN antibody; DKCB6 antibody; PFBMFT4 antibody; poly-specific ribonuclease antibody
-
Isotype
Rabbit IgG
-
Preparation
Antigen: Recombinant fusion protein containing a sequence corresponding to amino acids 1-280 of human PARN (NP_002573.1).
-
Clonality
Polyclonal
-
Formulation
PBS with 0.02% sodium azide, 50% glycerol, pH7.3.
-
Storage instructions
Store at -20℃. Avoid freeze / thaw cycles.
-
Applications
WB 1:500 - 1:2000
IF 1:50 - 1:100 -
Validations
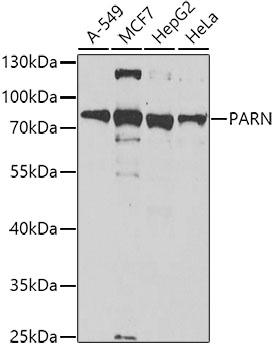
Western blot - PARN Polyclonal Antibody
Western blot analysis of extracts of various cell lines, using PARN antibody at 1:1000 dilution.Secondary antibody: HRP Goat Anti-Rabbit IgG (H+L) at 1:10000 dilution.Lysates/proteins: 25ug per lane.Blocking buffer: 3% nonfat dry milk in TBST.Detection: ECL Basic Kit .Exposure time: 150s.
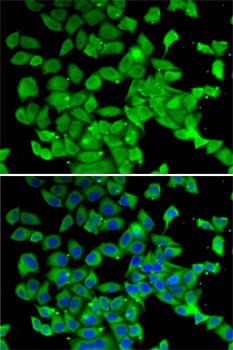
Immunofluorescence - PARN Polyclonal Antibody
Immunofluorescence analysis of MCF7 cells using PARN antibody . Blue: DAPI for nuclear staining.
-
Background
3'-exoribonuclease that has a preference for poly(A) tails of mRNAs, thereby efficiently degrading poly(A) tails. Exonucleolytic degradation of the poly(A) tail is often the first step in the decay of eukaryotic mRNAs and is also used to silence certain maternal mRNAs translationally during oocyte maturation and early embryonic development. Interacts with both the 3'-end poly(A) tail and the 5'-end cap structure during degradation, the interaction with the cap structure being required for an efficient degradation of poly(A) tails. Involved in nonsense-mediated mRNA decay, a critical process of selective degradation of mRNAs that contain premature stop codons. Also involved in degradation of inherently unstable mRNAs that contain AU-rich elements (AREs) in their 3'-UTR, possibly via its interaction with KHSRP. Probably mediates the removal of poly(A) tails of AREs mRNAs, which constitutes the first step of destabilization. Also able to recognize and trim poly(A) tails of microRNAs such as MIR21 and H/ACA box snoRNAs (small nucleolar RNAs) leading to microRNAs degradation or snoRNA increased stability.
Related Products / Services
Please note: All products are "FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY AND ARE NOT INTENDED FOR DIAGNOSTIC OR THERAPEUTIC USE"
