-
Product Name
PABPC1 Polyclonal Antibody
- Documents
-
Description
Polyclonal antibody to PABPC1
-
Tested applications
WB, IHC, IF
-
Species reactivity
Human, Mouse, Rat
-
Alternative names
PABPC1 antibody; PAB1 antibody; PABP antibody; PABP1 antibody; PABPC2 antibody; PABPL1 antibody; polyadenylate-binding protein 1 antibody
-
Isotype
Rabbit IgG
-
Preparation
Antigen: A synthetic peptide corresponding to a sequence within amino acids 350-450 of human PABPC1 (NP_002559.2).
-
Clonality
Polyclonal
-
Formulation
PBS with 0.02% sodium azide, 50% glycerol, pH7.3.
-
Storage instructions
Store at -20℃. Avoid freeze / thaw cycles.
-
Applications
WB 1:500 - 1:2000
IHC 1:50 - 1:100
IF 1:50 - 1:100 -
Validations
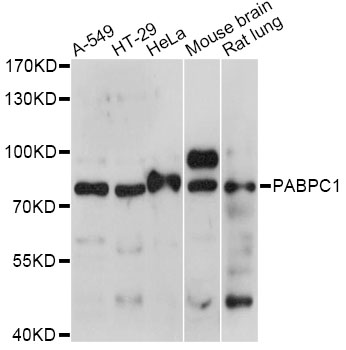
Western blot - PABPC1 Polyclonal Antibody
Western blot analysis of extracts of various cell lines, using PABPC1 antibody at 1:1000 dilution.Secondary antibody: HRP Goat Anti-Rabbit IgG (H+L) at 1:10000 dilution.Lysates/proteins: 25ug per lane.Blocking buffer: 3% nonfat dry milk in TBST.Detection: ECL Basic Kit .Exposure time: 30s.
-
Background
Binds the poly(A) tail of mRNA, including that of its own transcript. May be involved in cytoplasmic regulatory processes of mRNA metabolism such as pre-mRNA splicing. Its function in translational initiation regulation can either be enhanced by PAIP1 or repressed by PAIP2. Can probably bind to cytoplasmic RNA sequences other than poly(A) in vivo. Involved in translationally coupled mRNA turnover. Implicated with other RNA-binding proteins in the cytoplasmic deadenylation/translational and decay interplay of the FOS mRNA mediated by the major coding-region determinant of instability (mCRD) domain. Involved in regulation of nonsense-mediated decay (NMD) of mRNAs containing premature stop codons; for the recognition of premature termination codons (PTC) and initiation of NMD a competitive interaction between UPF1 and PABPC1 with the ribosome-bound release factors is proposed. By binding to long poly(A) tails, may protect them from uridylation by ZCCHC6/ZCCHC11 and hence contribute to mRNA stability. Positively regulates the replication of dengue virus (DENV).
Related Products / Services
Please note: All products are "FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY AND ARE NOT INTENDED FOR DIAGNOSTIC OR THERAPEUTIC USE"
