-
Product Name
NUMA1 Polyclonal Antibody
- Documents
-
Description
Polyclonal antibody to NUMA1
-
Tested applications
WB, IHC, IF
-
Species reactivity
Human, Mouse, Rat
-
Alternative names
NUMA1 antibody; NMP-22 antibody; NUMA antibody; nuclear mitotic apparatus protein 1 antibody
-
Isotype
Rabbit IgG
-
Preparation
Antigen: Recombinant fusion protein containing a sequence corresponding to amino acids 1-309 of human NUMA1 (NP_006176.2).
-
Clonality
Polyclonal
-
Formulation
PBS with 0.02% sodium azide, 50% glycerol, pH7.3.
-
Storage instructions
Store at -20℃. Avoid freeze / thaw cycles.
-
Applications
WB 1:200 - 1:1000
IHC 1:50 - 1:100
IF 1:50 - 1:100 -
Validations
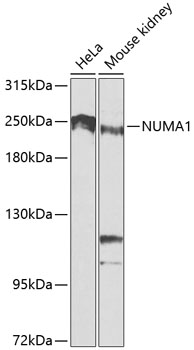
Western blot - NUMA1 Polyclonal Antibody
Western blot analysis of extracts of various cell lines, using NUMA1 antibody at 1:1000 dilution.Secondary antibody: HRP Goat Anti-Rabbit IgG (H+L) at 1:10000 dilution.Lysates/proteins: 25ug per lane.Blocking buffer: 3% nonfat dry milk in TBST.Detection: ECL Basic Kit .Exposure time: 90s.
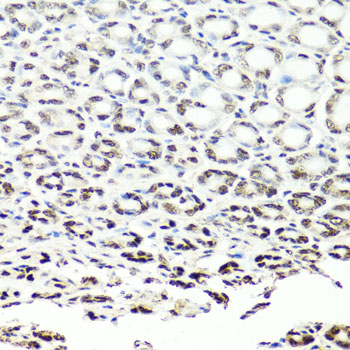
Immunohistochemistry - NUMA1 Polyclonal Antibody
Immunohistochemistry of paraffin-embedded human stomach using NUMA1 antibody at dilution of 1:100 (40x lens).
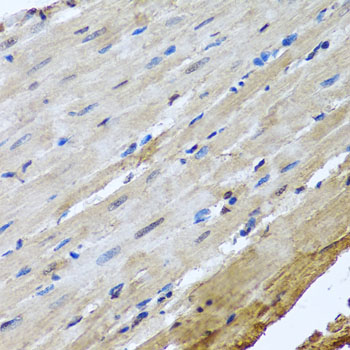
Immunohistochemistry - NUMA1 Polyclonal Antibody
Immunohistochemistry of paraffin-embedded rat heart using NUMA1 antibody at dilution of 1:100 (40x lens).
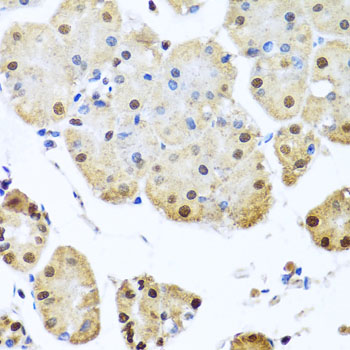
Immunohistochemistry - NUMA1 Polyclonal Antibody
Immunohistochemistry of paraffin-embedded mouse stomach using NUMA1 antibody at dilution of 1:100 (40x lens).
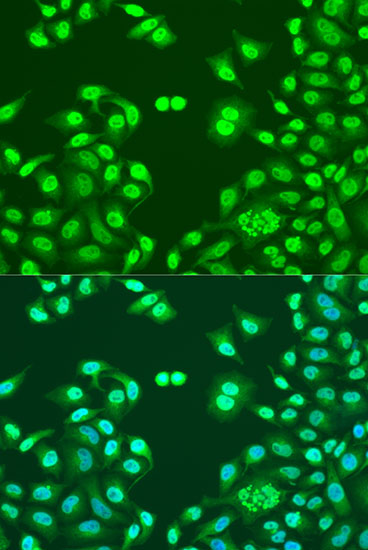
Immunofluorescence - NUMA1 Polyclonal Antibody
Immunofluorescence analysis of U2OS cells using NUMA1 antibody at dilution of 1:100. Blue: DAPI for nuclear staining.
-
Background
Microtubule (MT)-binding protein that plays a role in the formation and maintenance of the spindle poles and the alignement and the segregation of chromosomes during mitotic cell division. Functions to tether the minus ends of MTs at the spindle poles, which is critical for the establishment and maintenance of the spindle poles. Plays a role in the establishment of the mitotic spindle orientation during metaphase and elongation during anaphase in a dynein-dynactin-dependent manner. In metaphase, part of a ternary complex composed of GPSM2 and G(i) alpha proteins, that regulates the recruitment and anchorage of the dynein-dynactin complex in the mitotic cell cortex regions situated above the two spindle poles, and hence regulates the correct oritentation of the mitotic spindle. During anaphase, mediates the recruitment and accumulation of the dynein-dynactin complex at the cell membrane of the polar cortical region through direct association with phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate (PI(4,5)P2), and hence participates in the regulation of the spindle elongation and chromosome segregation. Binds also to other polyanionic phosphoinositides, such as phosphatidylinositol 3-phosphate (PIP), lysophosphatidic acid (LPA) and phosphatidylinositol triphosphate (PIP3), in vitro. Also required for proper orientation of the mitotic spindle during asymmetric cell divisions. Plays a role in mitotic MT aster assembly. Involved in anastral spindle assembly. Positively regulates TNKS protein localization to spindle poles in mitosis. Highly abundant component of the nuclear matrix where it may serve a non-mitotic structural role, occupies the majority of the nuclear volume. Required for epidermal differentiation and hair follicle morphogenesis (By similarity).
Related Products / Services
Please note: All products are "FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY AND ARE NOT INTENDED FOR DIAGNOSTIC OR THERAPEUTIC USE"
