-
Product Name
NCAM1/CD56 antibody
- Documents
-
Description
NCAM1/CD56 Mouse Monoclonal antibody. Positive WB detected in Human brain. Positive IHC detected in human lung cancer tissue. Observed molecular weight by Western-blot: 140 kDa
-
Tested applications
ELISA, WB, IHC
-
Species reactivity
Human,Mouse; other species not tested.
-
Alternative names
CD56 antibody; MSK39 antibody; N CAM 1 antibody; NCAM antibody; NCAM 1 antibody; NCAM1 antibody
-
Isotype
Mouse IgG1
-
Preparation
This antibody was obtained by immunization of NCAM1/CD56 recombinant protein (Accession Number: NM_181351). Purification method: Protein G purified.
-
Clonality
Monoclonal
-
Formulation
PBS with 0.02% sodium azide and 50% glycerol pH 7.3.
-
Storage instructions
Store at -20℃. DO NOT ALIQUOT
-
Applications
Recommended Dilution:
WB: 1:500-1:5000
IHC: 1:20-1:200
-
Validations
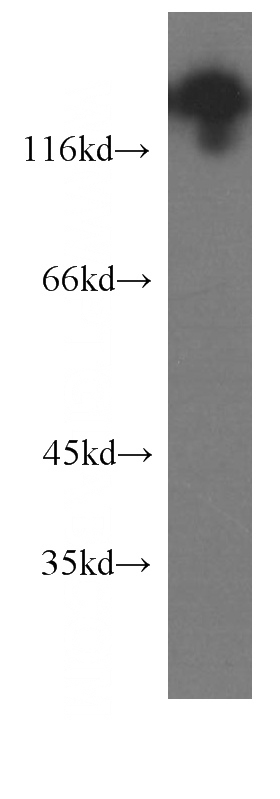
human brain tissue were subjected to SDS PAGE followed by western blot with Catalog No:107324(NCAM1 antibody) at dilution of 1:1000
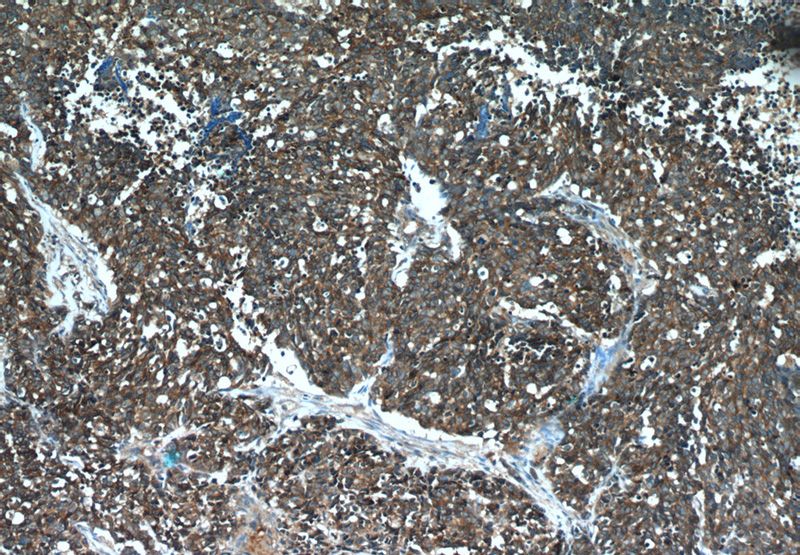

Immunohistochemical of paraffin-embedded human lung cancer using Catalog No:107324(NCAM1 antibody) at dilution of 1:50 (under 10x lens)
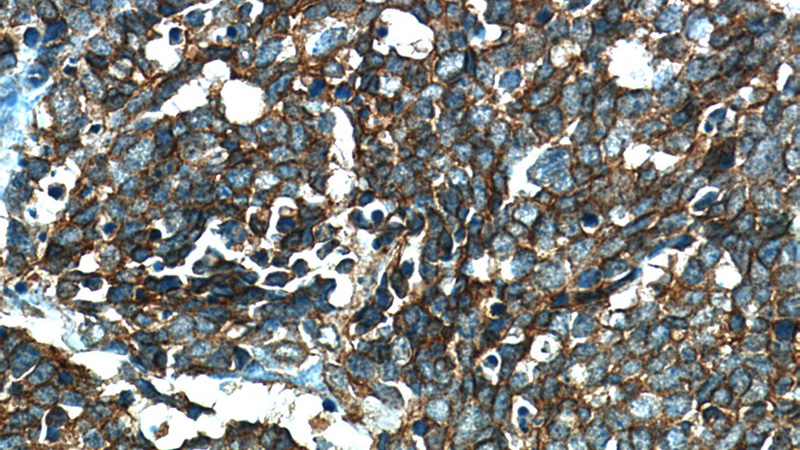
Immunohistochemical of paraffin-embedded human lung cancer using Catalog No:107324(NCAM1 antibody) at dilution of 1:50 (under 40x lens)
-
Background
Neural cell adhesion molecule 1 (NCAM1, also known as CD56) is a cell adhesion glycoprotein of the immunoglobulin (Ig) superfamily. It is a multifunction protein involved in synaptic plasticity, neurodevelopment, and neurogenesis. NCAM1 is expressed on human neurones, glial cells, skeletal muscle cells, NK cells and a subset of T cells, and the expression is observed in a wide variety human tumors, including myeloma, myeloid leukemia, neuroendocrine tumors, Wilms' tumor, neuroblastoma, and NK/T cell lymphomas. Three major isoforms of NCAM1, with molecular masses of 120, 140, and 180 kDa, are generated by alternative splicing of mRNA (PMID: 9696812). The glycosylphosphatidylinositol (GPI)-anchored NCAM120 and the transmembrane NCAM140 and NCAM180 consist of five Ig-like domains and two fibronection-type III repeats (FNIII). All three forms can be posttranslationally modified by addition of polysialic acid (PSA) (PMID: 14976519). Several other isofroms have also been described (PMID: 1856291).
Related Products / Services
Please note: All products are "FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY AND ARE NOT INTENDED FOR DIAGNOSTIC OR THERAPEUTIC USE"
