-
Product Name
Human KIR2DL3 (CD158b2) (His Tag) recombinant protein
- Documents
-
Description
Killer cell immunoglobulin-like receptor 2DL3, also known as CD158 antigen-like family member B2, KIR-023GB, Killer inhibitory receptor cl 2-3, MHC class I NK cell receptor, NKAT2a, NKAT2b, Natural killer-associated transcript 2, p58 natural killer cell receptor clone CL-6, p58.2 MHC class-I-specific NK receptor, CD158b2 and KIR2DL3, is a single-pass type I membrane protein which belongs to the immunoglobulin superfamily. KIR2DL3 contains 2 Ig-like C2-type (immunoglobulin-like) domains. KIR2DL3 interacts with ARRB2. KIR2DL3 is a receptor on natural killer (NK) cells for HLA-C alleles (HLA-Cw1, HLA-Cw3 and HLA-Cw7). KIR2DL3 inhibits the activity of NK cells thus preventing cell lysis.
-
Protein name
Natural killer cell inhibitory receptor
-
Protein short names
GL183; NKAT; MGC129943; KIRCL23; CD158B2; KIR-023GB; KIR2DL3; CU464054.1; CD158B; KIR-K7B; KIR-K7C
-
Uniprot ID
Q32WE4
-
Gene Name
KIR2DL3
-
Source/Expression Host
Human Cells
-
Expression Plasmid/cDNA
A DNA sequence encoding the human KIR2DL3 (AAX23102.1) extracellular domain (Met 1-His 245) was fused with a polyhistidine tag at the C-terminus.
-
Protein Species
Human
-
Molecular weight
The secreted recombinant human KIR2DL3 consists of 235 amino acids and has a predicted molecular mass of 25.9 kDa. As a result of glycosylation, the apparent molecular mass of rh KIR2DL3 is approximately 45 kDa in SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions.
-
Purity
> 98 % as determined by SDS-PAGE
-
Validations
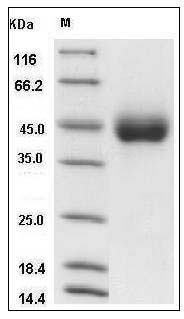
Human KIR2DL3 / CD158B2 / NKAT-2 Protein (His Tag) SDS-PAGE
Related Products / Services
Please note: All products are "FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY AND ARE NOT INTENDED FOR DIAGNOSTIC OR THERAPEUTIC USE"
