-
Product Name
MYOG Polyclonal Antibody
- Documents
-
Description
Polyclonal antibody to MYOG
-
Tested applications
WB, IF
-
Species reactivity
Mouse, Rat
-
Alternative names
MYOG antibody; MYF4 antibody; bHLHc3 antibody; myf-4 antibody; myogenin antibody
-
Isotype
Rabbit IgG
-
Preparation
Antigen: Recombinant fusion protein containing a sequence corresponding to amino acids 1-1-224 of human MYOG (NP_002470.2).
-
Clonality
Polyclonal
-
Formulation
PBS with 0.02% sodium azide, 50% glycerol, pH7.3.
-
Storage instructions
Store at -20℃. Avoid freeze / thaw cycles.
-
Applications
WB 1:500 - 1:2000
IF 1:50 - 1:200 -
Validations
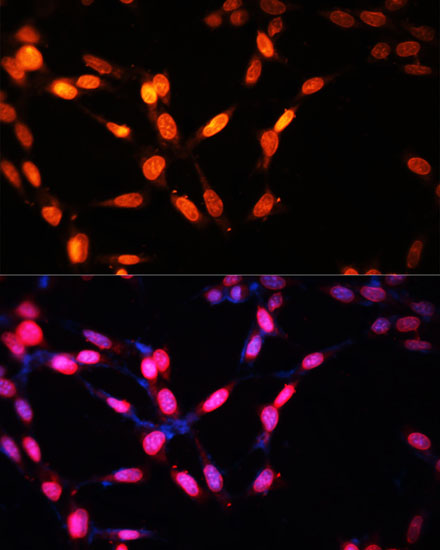
Immunofluorescence - MYOG Polyclonal Antibody
Immunofluorescence analysis of NIH/3T3 cells using MYOG antibody at dilution of 1:100. Blue: DAPI for nuclear staining.
-
Background
Acts as a transcriptional activator that promotes transcription of muscle-specific target genes and plays a role in muscle differentiation, cell cycle exit and muscle atrophy. Essential for the development of functional embryonic skeletal fiber muscle differentiation. However is dispensable for postnatal skeletal muscle growth; phosphorylation by CAMK2G inhibits its transcriptional activity in respons to muscle activity. Required for the recruitment of the FACT complex to muscle-specific promoter regions, thus promoting gene expression initiation. During terminal myoblast differentiation, plays a role as a strong activator of transcription at loci with an open chromatin structure previously initiated by MYOD1. Together with MYF5 and MYOD1, co-occupies muscle-specific gene promoter core regions during myogenesis. Cooperates also with myocyte-specific enhancer factor MEF2D and BRG1-dependent recruitment of SWI/SNF chromatin-remodeling enzymes to alter chromatin structure at myogenic late gene promoters. Facilitates cell cycle exit during terminal muscle differentiation through the up-regulation of miR-20a expression, which in turn represses genes involved in cell cycle progression. Binds to the E-box containing (E1) promoter region of the miR-20a gene. Plays also a role in preventing reversal of muscle cell differentiation. Contributes to the atrophy-related gene expression in adult denervated muscles. Induces fibroblasts to differentiate into myoblasts (By similarity).
Related Products / Services
Please note: All products are "FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY AND ARE NOT INTENDED FOR DIAGNOSTIC OR THERAPEUTIC USE"
