-
Product Name
MYO7A antibody
- Documents
-
Description
MYO7A Rabbit Polyclonal antibody. Positive WB detected in L02 cells, A431 cells. Positive IF detected in HepG2. Observed molecular weight by Western-blot: 160-255kd
-
Tested applications
ELISA, WB, IF
-
Species reactivity
human, mouse, rat; other species not tested.
-
Alternative names
MYO7A antibody; NSRD2 antibody; USH1B antibody; MYOVIIA antibody; DFNA11 antibody
-
Isotype
Rabbit IgG
-
Preparation
This antibody was obtained by immunization of Peptide (Accession Number: NM_000260). Purification method: Antigen affinity purified.
-
Clonality
Polyclonal
-
Formulation
PBS with 0.02% sodium azide and 50% glycerol pH 7.3.
-
Storage instructions
Store at -20℃. DO NOT ALIQUOT
-
Applications
Recommended Dilution:
WB: 1:500-1:5000
IF: 1:10-1:100
-
Validations

L02 cells were subjected to SDS PAGE followed by western blot with Catalog No:112986(MYO7A antibody) at dilution of 1:500
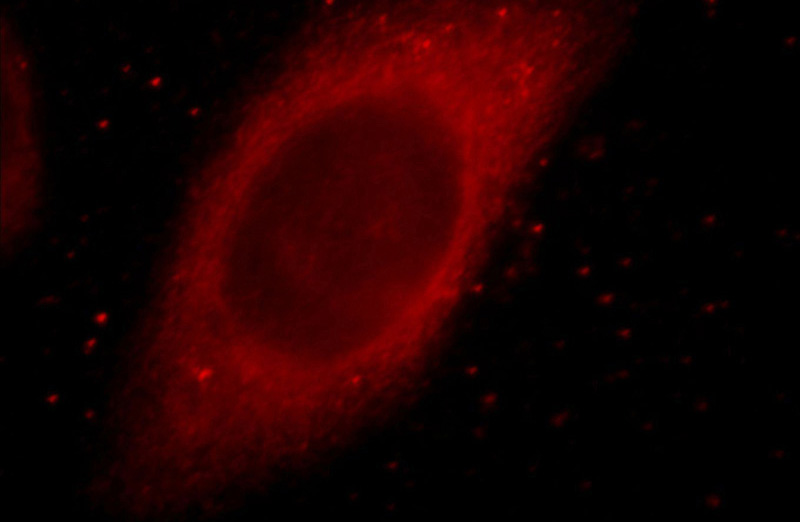
Immunofluorescent analysis of HepG2 cells, using MYO7A antibody Catalog No:112986 at 1:25 dilution and Rhodamine-labeled goat anti-rabbit IgG (red).
-
Background
MYO7A, also named a USH1B, is one of myosins protein which are actin-based motor molecules with ATPase activity. Unconventional myosins serve in intracellular movements. Their highly divergent tails are presumed to bind to membranous compartments, which would be moved relative to actin filaments. In retina, MYO7A might play a role in trafficking of ribbon-synaptic vesicle complexes and renewal of the outer photoreceptors disks. In inner ear, it might maintain the rigidity of stereocilia during the dynamic movements of the bundle. It is involved in hair-cell vesicle trafficking of aminoglycosides, which are known to induce ototoxicity. Defects in MYO7A are the cause of Usher syndrome type 1B (USH1B). Defects in MYO7A are the cause of deafness autosomal recessive type 2 (DFNB2). Defects in MYO7A are the cause of deafness autosomal dominant type 11 (DFNA11). The antibody is specific to MYO7A.
Related Products / Services
Please note: All products are "FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY AND ARE NOT INTENDED FOR DIAGNOSTIC OR THERAPEUTIC USE"
