-
Product Name
MLYCD antibody
- Documents
-
Description
MLYCD Rabbit Polyclonal antibody. Positive IHC detected in human kidney tissue, human heart tissue, human liver tissue. Positive IF detected in HepG2 cells. Positive IP detected in mouse heart tissue. Positive WB detected in human testis tissue, HEK-293 cells, HepG2 cells, HT-1080 cells, human heart tissue, L02 cells, mouse brain tissue, mouse heart tissue, mouse testis tissue, rat brain tissue. Observed molecular weight by Western-blot: 50kd,55kd,66kd
-
Tested applications
ELISA, WB, IHC, IF, IP
-
Species reactivity
Human,Mouse,Rat; other species not tested.
-
Alternative names
malonyl CoA decarboxylase antibody; MCD antibody; MLYCD antibody
-
Isotype
Rabbit IgG
-
Preparation
This antibody was obtained by immunization of MLYCD recombinant protein (Accession Number: BC000286). Purification method: Antigen affinity purified.
-
Clonality
Polyclonal
-
Formulation
PBS with 0.02% sodium azide and 50% glycerol pH 7.3.
-
Storage instructions
Store at -20℃. DO NOT ALIQUOT
-
Applications
Recommended Dilution:
WB: 1:500-1:5000
IP: 1:200-1:2000
IHC: 1:20-1:200
IF: 1:20-1:200
-
Validations
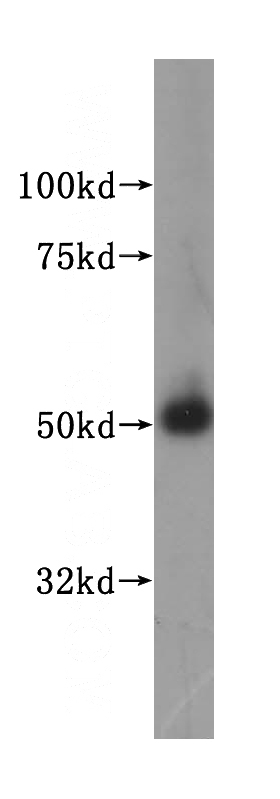
human testis tissue were subjected to SDS PAGE followed by western blot with Catalog No:112689(MLYCD antibody) at dilution of 1:400
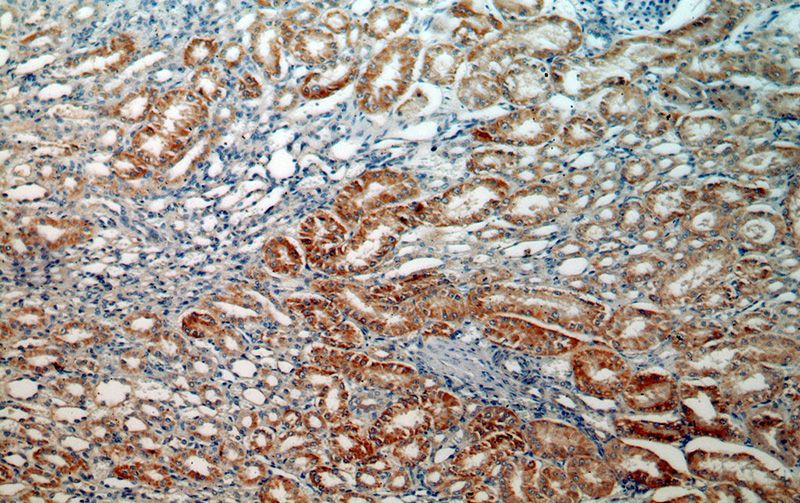
Immunohistochemical of paraffin-embedded human kidney using Catalog No:112689(MLYCD antibody) at dilution of 1:50 (under 10x lens)
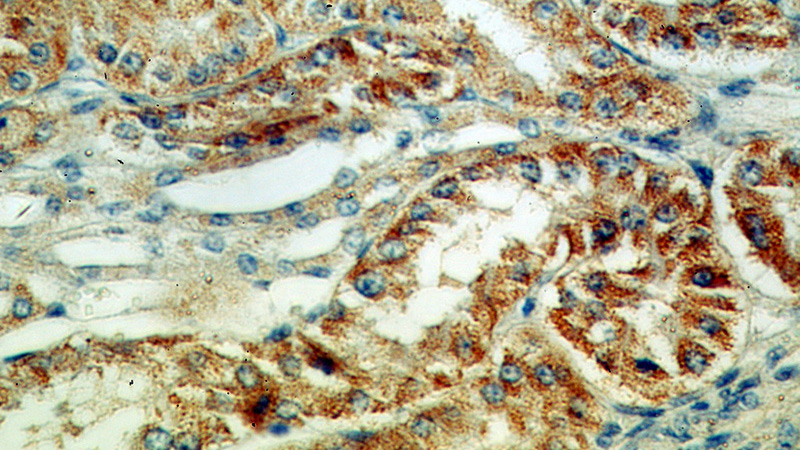
Immunohistochemical of paraffin-embedded human kidney using Catalog No:112689(MLYCD antibody) at dilution of 1:50 (under 40x lens)
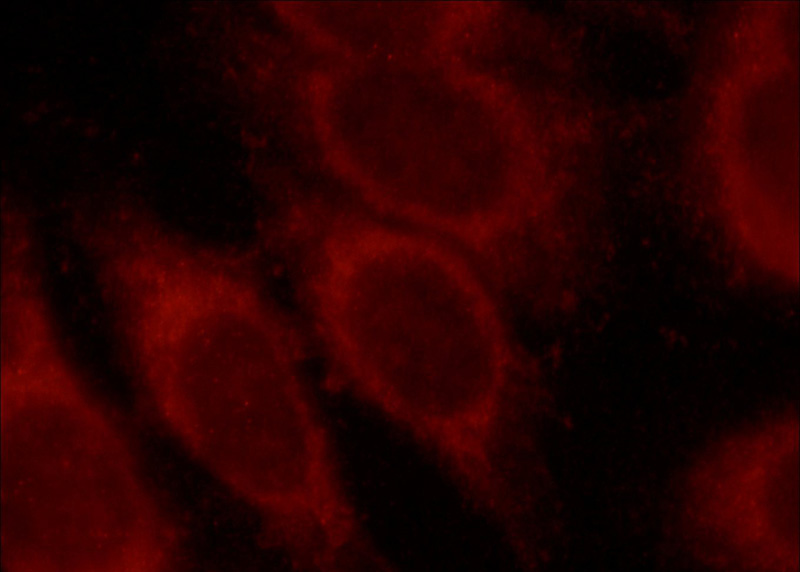
Immunofluorescent analysis of HepG2 cells, using MLYCD antibody Catalog No:112689 at 1:50 dilution and Rhodamine-labeled goat anti-rabbit IgG (red).
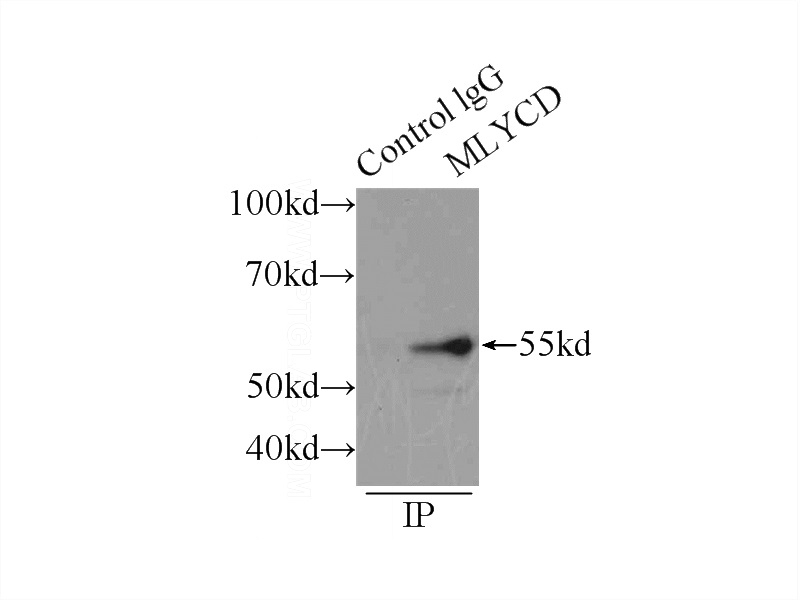
IP Result of anti-MLYCD (IP:Catalog No:112689, 4ug; Detection:Catalog No:112689 1:500) with mouse heart tissue lysate 5000ug.
-
Background
MLYCD, also named as MCD, is a 50-55 kDa protein. It is an enzyme that catalyzes the conversion of malonyl-CoA to acetyl-CoA. In the fatty acid biosynthesis MCD selectively removes malonyl-CoA and thus assures that methyl-malonyl-CoA is the only chain elongating substrate for fatty acid synthase and that fatty acids with multiple methyl side chains are produced. In peroxisomes it may be involved in degrading intraperoxisomal malonyl-CoA, which is generated by the peroxisomal beta-oxidation of odd chain-length dicarboxylic fatty acids. 66 kDa MLYCD protein has been identified in normal cell lines. Some patients give the 68-83 kDa smeary band. (PMID:12955715)
-
References
- Hyyti OM, Ledee D, Ning XH, Ge M, Portman MA. Aging impairs myocardial fatty acid and ketone oxidation and modifies cardiac functional and metabolic responses to insulin in mice. American journal of physiology. Heart and circulatory physiology. 299(3):H868-75. 2010.
- Stride N, Larsen S, Treebak JT. 5'-AMP Activated Protein Kinase is Involved in the Regulation of Myocardial β-Oxidative Capacity in Mice. Frontiers in physiology. 3:33. 2012.
- Olson AK, Ledee D, Iwamoto K. C-Myc induced compensated cardiac hypertrophy increases free fatty acid utilization for the citric acid cycle. Journal of molecular and cellular cardiology. 55:156-64. 2013.
- Polinati PP, Valanne L, Tyni T. Malonyl-CoA decarboxylase deficiency: long-term follow-up of a patient new clinical features and novel mutations. Brain & development. 37(1):107-13. 2015.
- Liu Y, He Y, Jin A. Ribosomal protein-Mdm2-p53 pathway coordinates nutrient stress with lipid metabolism by regulating MCD and promoting fatty acid oxidation. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 111(23):E2414-22. 2014.
- Ledee D, Smith L, Bruce M. c-Myc Alters Substrate Utilization and O-GlcNAc Protein Posttranslational Modifications without Altering Cardiac Function during Early Aortic Constriction. PloS one. 10(8):e0135262. 2015.
- Zhang H, Li Y, Hu J. Effect of Creosote Bush-Derived NDGA on Expression of Genes Involved in Lipid Metabolism in Liver of High-Fructose Fed Rats: Relevance to NDGA Amelioration of Hypertriglyceridemia and Hepatic Steatosis. PloS one. 10(9):e0138203. 2015.
- Wang MD, Wu H, Fu GB. Acetyl-CoA carboxylase α promotion of glucose-mediated fatty acid synthesis enhances survival of hepatocellular carcinoma in mice and patients. Hepatology (Baltimore, Md.). 2015.
Related Products / Services
Please note: All products are "FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY AND ARE NOT INTENDED FOR DIAGNOSTIC OR THERAPEUTIC USE"
