-
Product Name
MGAT5 Polyclonal Antibody
- Documents
-
Description
Polyclonal antibody to MGAT5
-
Tested applications
WB
-
Species reactivity
Human, Mouse
-
Alternative names
MGAT5 antibody; GNT-V antibody; GNT-VA antibody; alpha-1,6-mannosylglycoprotein 6-beta-N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase A antibody
-
Isotype
Rabbit IgG
-
Preparation
Antigen: Recombinant fusion protein containing a sequence corresponding to amino acids 627-741 of human MGAT5 (NP_002401.1).
-
Clonality
Polyclonal
-
Formulation
PBS with 0.02% sodium azide, 50% glycerol, pH7.3.
-
Storage instructions
Store at -20℃. Avoid freeze / thaw cycles.
-
Applications
WB 1:500 - 1:2000
-
Validations
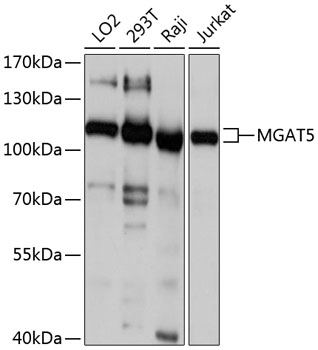
Western blot - MGAT5 Polyclonal Antibody
Western blot analysis of extracts of various cell lines, using MGAT5 antibody at 1:1000 dilution.Secondary antibody: HRP Goat Anti-Rabbit IgG (H+L) at 1:10000 dilution.Lysates/proteins: 25ug per lane.Blocking buffer: 3% nonfat dry milk in TBST.Detection: ECL Basic Kit .Exposure time: 1s.
-
Background
Catalyzes the addition of N-acetylglucosamine (GlcNAc) in beta 1-6 linkage to the alpha-linked mannose of biantennary N-linked oligosaccharides. Catalyzes an important step in the biosynthesis of branched, complex-type N-glycans, such as those found on EGFR, TGFR (TGF-beta receptor) and CDH2. Via its role in the biosynthesis of complex N-glycans, plays an important role in the activation of cellular signaling pathways, reorganization of the actin cytoskeleton, cell-cell adhesion and cell migration. MGAT5-dependent EGFR N-glycosylation enhances the interaction between EGFR and LGALS3 and thereby prevents rapid EGFR endocytosis and prolongs EGFR signaling. Required for efficient interaction between TGFB1 and its receptor. Enhances activation of intracellular signaling pathways by several types of growth factors, including FGF2, PDGF, IGF, TGFB1 and EGF. MGAT5-dependent CDH2 N-glycosylation inhibits CDH2-mediated homotypic cell-cell adhesion and contributes to the regulation of downstream signaling pathways. Promotes cell migration. Contributes to the regulation of the inflammatory response. MGAT5-dependent TCR N-glycosylation enhances the interaction between TCR and LGALS3, limits agonist-induced TCR clustering, and thereby dampens TCR-mediated responses to antigens. Required for normal leukocyte evasation and accumulation at sites of inflammation (By similarity). Inhibits attachment of monocytes to the vascular endothelium and subsequent monocyte diapedesis.; Secreted alpha-1,6-mannosylglycoprotein 6-beta-N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase A: Promotes proliferation of umbilical vein endothelial cells and angiogenesis, at least in part by promoting the release of the growth factor FGF2 from the extracellular matrix.
Related Products / Services
Please note: All products are "FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY AND ARE NOT INTENDED FOR DIAGNOSTIC OR THERAPEUTIC USE"
