-
Product Name
LRP4 Polyclonal Antibody
- Documents
-
Description
Polyclonal antibody to LRP4
-
Tested applications
WB
-
Species reactivity
Human, Mouse
-
Alternative names
LRP4 antibody; CLSS antibody; CMS17 antibody; LRP-4 antibody; LRP10 antibody; MEGF7 antibody; SOST2 antibody; LDL receptor related protein 4 antibody
-
Isotype
Rabbit IgG
-
Preparation
Antigen: Recombinant fusion protein containing a sequence corresponding to amino acids 1500-1725 of human LRP4 (NP_002325.2).
-
Clonality
Polyclonal
-
Formulation
PBS with 0.02% sodium azide, 50% glycerol, pH7.3.
-
Storage instructions
Store at -20℃. Avoid freeze / thaw cycles.
-
Applications
WB 1:500 - 1:2000
-
Validations
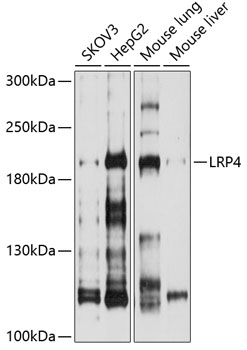
Western blot - LRP4 Polyclonal Antibody
Western blot analysis of extracts of various cell lines, using LRP4 antibody at 1:1000 dilution.Secondary antibody: HRP Goat Anti-Rabbit IgG (H+L) at 1:10000 dilution.Lysates/proteins: 25ug per lane.Blocking buffer: 3% nonfat dry milk in TBST.
-
Background
Mediates SOST-dependent inhibition of bone formation. Functions as a specific facilitator of SOST-mediated inhibition of Wnt signaling. Plays a key role in the formation and the maintenance of the neuromuscular junction (NMJ), the synapse between motor neuron and skeletal muscle. Directly binds AGRIN and recruits it to the MUSK signaling complex. Mediates the AGRIN-induced phosphorylation of MUSK, the kinase of the complex. The activation of MUSK in myotubes induces the formation of NMJ by regulating different processes including the transcription of specific genes and the clustering of AChR in the postsynaptic membrane. Alternatively, may be involved in the negative regulation of the canonical Wnt signaling pathway, being able to antagonize the LRP6-mediated activation of this pathway. More generally, has been proposed to function as a cell surface endocytic receptor binding and internalizing extracellular ligands for degradation by lysosomes. May play an essential role in the process of digit differentiation (By similarity).
Related Products / Services
Please note: All products are "FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY AND ARE NOT INTENDED FOR DIAGNOSTIC OR THERAPEUTIC USE"
