-
Product Name
KCNK1 Polyclonal Antibody
- Documents
-
Description
Polyclonal antibody to KCNK1
-
Tested applications
WB, IHC
-
Species reactivity
Human, Mouse, Rat
-
Alternative names
KCNK1 antibody; DPK antibody; HOHO antibody; K2P1 antibody; K2p1.1 antibody; KCNO1 antibody; TWIK-1 antibody; TWIK1 antibody; potassium channel subfamily K member 1 antibody
-
Isotype
Rabbit IgG
-
Preparation
Antigen: Recombinant fusion protein containing a sequence corresponding to amino acids 267-336 of human KCNK1 (NP_002236.1).
-
Clonality
Polyclonal
-
Formulation
PBS with 0.02% sodium azide, 50% glycerol, pH7.3.
-
Storage instructions
Store at -20℃. Avoid freeze / thaw cycles.
-
Applications
WB 1:500 - 1:2000
IHC 1:50 - 1:200 -
Validations
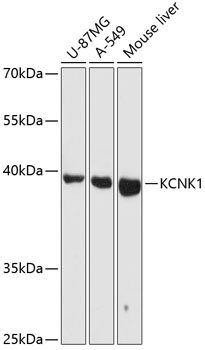
Western blot - KCNK1 Polyclonal Antibody
Western blot analysis of extracts of various cell lines, using KCNK1 antibody at 1:3000 dilution.Secondary antibody: HRP Goat Anti-Rabbit IgG (H+L) at 1:10000 dilution.Lysates/proteins: 25ug per lane.Blocking buffer: 3% nonfat dry milk in TBST.Detection: ECL Basic Kit .Exposure time: 30s.
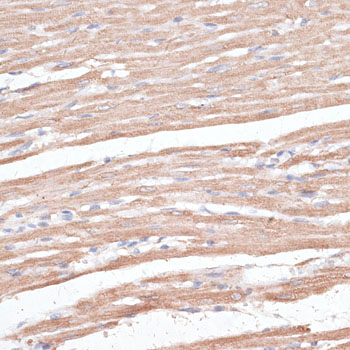
Immunohistochemistry - KCNK1 Polyclonal Antibody
Immunohistochemistry of paraffin-embedded rat heart using KCNK1 antibody at dilution of 1:100 (40x lens).
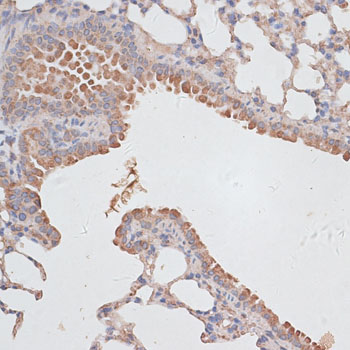
Immunohistochemistry - KCNK1 Polyclonal Antibody
Immunohistochemistry of paraffin-embedded mouse lung using KCNK1 antibody at dilution of 1:100 (40x lens).
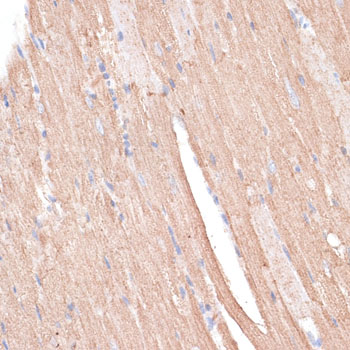
Immunohistochemistry - KCNK1 Polyclonal Antibody
Immunohistochemistry of paraffin-embedded mouse heart using KCNK1 antibody at dilution of 1:100 (40x lens).
-
Background
Ion channel that contributes to passive transmembrane potassium transport and to the regulation of the resting membrane potential in brain astrocytes, but also in kidney and in other tissues. Forms dimeric channels through which potassium ions pass in accordance with their electrochemical gradient. The channel is selective for K(+) ions at physiological potassium concentrations and at neutral pH, but becomes permeable to Na(+) at subphysiological K(+) levels and upon acidification of the extracellular medium. The homodimer has very low potassium channel activity, when expressed in heterologous systems, and can function as weakly inward rectifying potassium channel. Channel activity is modulated by activation of serotonin receptors (By similarity). Heterodimeric channels containing KCNK1 and KCNK2 have much higher activity, and may represent the predominant form in astrocytes (By similarity). Heterodimeric channels containing KCNK1 and KCNK3 or KCNK9 have much higher activity. Heterodimeric channels formed by KCNK1 and KCNK9 may contribute to halothane-sensitive currents. Mediates outward rectifying potassium currents in dentate gyrus granule cells and contributes to the regulation of their resting membrane potential (By similarity). Contributes to the regulation of action potential firing in dentate gyrus granule cells and down-regulates their intrinsic excitability (By similarity). In astrocytes, the heterodimer formed by KCNK1 and KCNK2 is required for rapid glutamate release in response to activation of G-protein coupled receptors, such as F2R and CNR1 (By similarity). Required for normal ion and water transport in the kidney (By similarity). Contributes to the regulation of the resting membrane potential of pancreatic beta cells (By similarity). The low channel activity of homodimeric KCNK1 may be due to sumoylation. The low channel activity may be due to rapid internalization from the cell membrane and retention in recycling endosomes.
Related Products / Services
Please note: All products are "FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY AND ARE NOT INTENDED FOR DIAGNOSTIC OR THERAPEUTIC USE"
