-
Product Name
JUN antibody
- Documents
-
Description
JUN Mouse Monoclonal antibody. Positive WB detected in RAW 264.7 cells, NIH/3T3 cells. Observed molecular weight by Western-blot: 39 kDa
-
Tested applications
ELISA, WB
-
Species reactivity
Human, Mouse; other species not tested.
-
Alternative names
Activator protein 1 antibody; AP 1 antibody; AP1 antibody; c Jun antibody; JUN antibody; jun oncogene antibody; P39 antibody; Proto oncogene c Jun antibody; Transcription factor AP 1 antibody
-
Isotype
Mouse IgG1
-
Preparation
This antibody was obtained by immunization of JUN recombinant protein (Accession Number: NM_002228). Purification method: Protein G purified.
-
Clonality
Monoclonal
-
Formulation
PBS with 0.02% sodium azide and 50% glycerol pH 7.3.
-
Storage instructions
Store at -20℃. DO NOT ALIQUOT
-
Applications
Recommended Dilution:
WB: 1:1000-1:10000
-
Validations
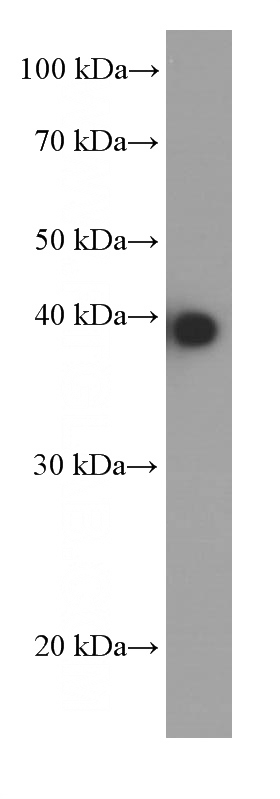
RAW 264.7 cells were subjected to SDS PAGE followed by western blot with Catalog No:107358(JUN Antibody) at dilution of 1:4000
-
Background
JUN is also named as c-Jun and AP1, belongs to the bZIP family and Jun subfamily. JUN, the most extensively studied protein of the activator protein-1 (AP-1) complex, is involved in numerous cell activities, such as proliferation, apoptosis, survival, tumorigenesis and tissue morphogenesis[PMID: 22180088]. JUN is a transcription factor that recognizes and binds to the enhancer heptamer motif 5'-TGA[CG]TCA-3'. It promotes activity of NR5A1 when phosphorylated by HIPK3 leading to increased steroidogenic gene expression upon cAMP signaling pathway stimulation. JUN is a basic leucine zipper (bZIP) transcription factor that acts as homo- or heterodimer, binding to DNA and regulating gene transcription[PMID: 9732876]. In additon, extracellular signals can induce post-translational modifications of JUN, resulting in altered transcriptional activity and target gene expression[PMID:8464713]. More over, it has uncovered multiple layers of a complex regulatory scheme in which JUN is able to crosstalk, amplify and integrate different signals for tissue development and disease. Jun is predominantly nuclear, ubiquitinated Jun colocalizes with lysosomal proteins[PMID: 15469925].
Related Products / Services
Please note: All products are "FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY AND ARE NOT INTENDED FOR DIAGNOSTIC OR THERAPEUTIC USE"
