-
Product Name
INHBC Polyclonal Antibody
- Documents
-
Description
Polyclonal antibody to INHBC
-
Tested applications
WB, IHC
-
Species reactivity
Human, Mouse, Rat
-
Alternative names
INHBC antibody; IHBC antibody; inhibin beta C chain antibody
-
Isotype
Rabbit IgG
-
Preparation
Antigen: Recombinant fusion protein containing a sequence corresponding to amino acids 103-352 of human INHBC (NP_005529.1).
-
Clonality
Polyclonal
-
Formulation
PBS with 0.02% sodium azide, 50% glycerol, pH7.3.
-
Storage instructions
Store at -20℃. Avoid freeze / thaw cycles.
-
Applications
WB 1:500 - 1:2000
IHC 1:100 - 1:200 -
Validations
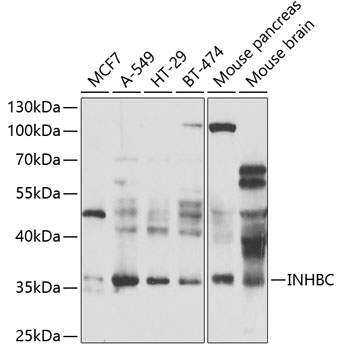
Western blot - INHBC Polyclonal Antibody
Western blot analysis of extracts of various cell lines, using INHBC antibody at 1:1000 dilution._Secondary antibody: HRP Goat Anti-Rabbit IgG (H+L) at 1:10000 dilution._Lysates/proteins: 25ug per lane._Blocking buffer: 3% nonfat dry milk in TBST._Detection: ECL Enhanced Kit ._Exposure time: 90s.
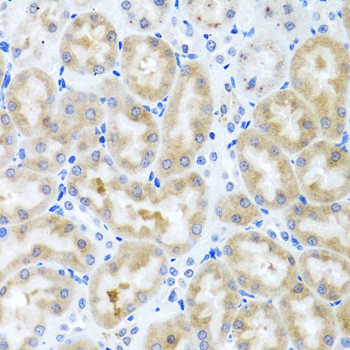
Immunohistochemistry - INHBC Polyclonal Antibody
Immunohistochemistry of paraffin-embedded rat kidney using INHBC antibody at dilution of 1:100 (40x lens).
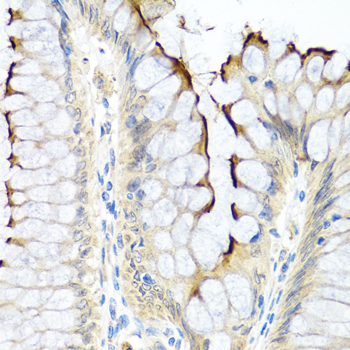
Immunohistochemistry - INHBC Polyclonal Antibody
Immunohistochemistry of paraffin-embedded human colon using INHBC antibody at dilution of 1:100 (40x lens).
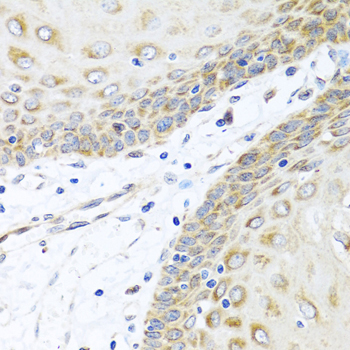
Immunohistochemistry - INHBC Polyclonal Antibody
Immunohistochemistry of paraffin-embedded human esophagus using INHBC antibody at dilution of 1:100 (40x lens).
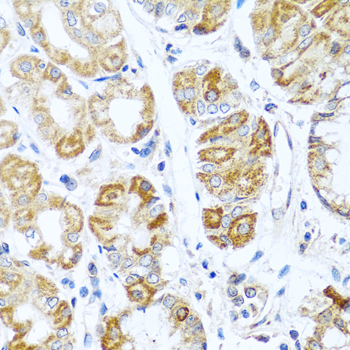
Immunohistochemistry - INHBC Polyclonal Antibody
Immunohistochemistry of paraffin-embedded human stomach using INHBC antibody at dilution of 1:100 (40x lens).
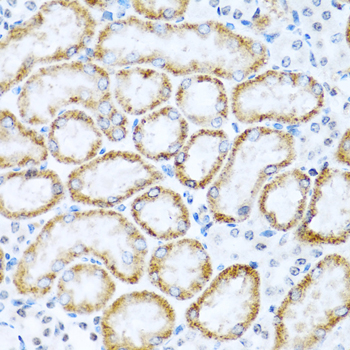
Immunohistochemistry - INHBC Polyclonal Antibody
Immunohistochemistry of paraffin-embedded mouse kidney using INHBC antibody at dilution of 1:100 (40x lens).
-
Background
Inhibins and activins inhibit and activate, respectively, the secretion of follitropin by the pituitary gland. Inhibins/activins are involved in regulating a number of diverse functions such as hypothalamic and pituitary hormone secretion, gonadal hormone secretion, germ cell development and maturation, erythroid differentiation, insulin secretion, nerve cell survival, embryonic axial development or bone growth, depending on their subunit composition. Inhibins appear to oppose the functions of activins.
Related Products / Services
Please note: All products are "FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY AND ARE NOT INTENDED FOR DIAGNOSTIC OR THERAPEUTIC USE"
