-
Product Name
Human OASL/TRIP14 (His tag) recombinant protein
- Documents
-
Description
2'-5'-oligoadenylate synthase-like protein (OASL) contains 2 ubiquitin-like domains, and belongs to the 2-5A synthase family. The ubiquitin-like domains are essential for its antiviral activity. OASL can be induced by type I interferon (IFN) and viruses, and expressed in most tissues such as primary blood Leukocytes and other hematopoietic system tissues, colon, stomach and to some extent in testis. OASL can specifically interacts with the ligand binding domain of the thyroid receptor (TR) without the presence of thyroid hormone. It does not have 2'-5'-OAS activity, but can bind double-stranded RNA. It also displays antiviral activity against encephalomyocarditis virus (EMCV) and hepatitis C virus (HCV) via an alternative antiviral pathway independent of RNase L.
-
Protein name
2'-5'-oligoadenylate synthetase like(OASL)
-
Protein short names
TRIP14
-
Uniprot ID
Q15646
-
Source/Expression Host
E. coli
-
Expression Plasmid/cDNA
A DNA sequence encoding the Human OASL/TRIP14 Met1-His100 is expressed with a 6His tag at the C-terminus.
-
Protein Species
Human
-
Purity
>95% as determined by SDS-PAGE.
-
Validations
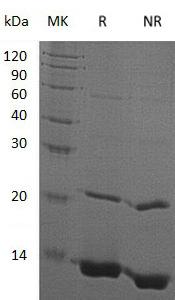
Human OASL/TRIP14 (His tag) recombinant protein
Related Products / Services
Please note: All products are "FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY AND ARE NOT INTENDED FOR DIAGNOSTIC OR THERAPEUTIC USE"
