-
Product Name
Human HDAC7 Recombinant protein (His tag)
- Documents
-
Description
Responsible for the deacetylation of lysine residues on the N-terminal part of the core histones (H2A, H2B, H3 and H4). Histone deacetylation gives a tag for epigenetic repression and plays an important role in transcriptional regulation, cell cycle progression and developmental events. Histone deacetylases act via the formation of large multiprotein complexes. Involved in muscle maturation by repressing transcription of myocyte enhancer factors such as MEF2A, MEF2B and MEF2C. During muscle differentiation, it shuttles into the cytoplasm, allowing the expression of myocyte enhancer factors (By similarity). May be involved in Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) latency, possibly by repressing the viral BZLF1 gene. Positively regulates the transcriptional repressor activity of FOXP3 (PubMed:17360565). {UniProtKB:Q8C2B3, PubMed:12239305, PubMed:17360565}.
-
Protein name
Histone deacetylase 7
-
Protein short names
HDAC7A
-
Uniprot ID
Q8WUI4
-
Gene Name
HDAC7; HDAC7A
-
Source/Expression Host
E. coli
-
Expression Plasmid/cDNA
A DNA sequence encoding the human HDAC7 (XP_054228220.1) 952-1035 aa was fused with the polyhistidine tag
-
Protein Species
Human
-
Activity
Not tested.
-
Validations
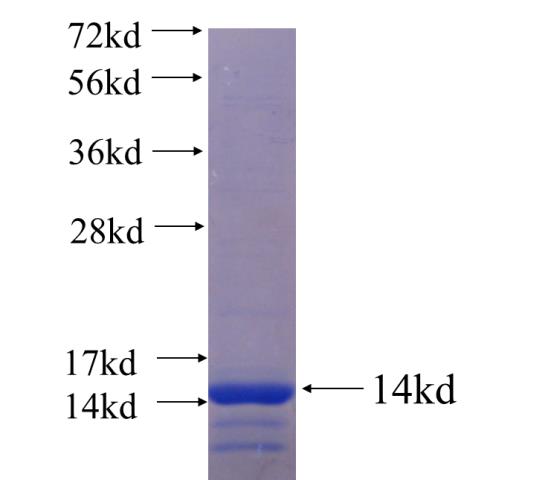
Recombinant human HDAC7 SDS-PAGE
Related Products / Services
Please note: All products are "FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY AND ARE NOT INTENDED FOR DIAGNOSTIC OR THERAPEUTIC USE"
