-
Product Name
HSPA13 antibody
- Documents
-
Description
HSPA13 Rabbit Polyclonal antibody. Positive IHC detected in human endometrial cancer tissue. Positive IP detected in HeLa cells. Positive WB detected in human brain tissue, HeLa cells. Observed molecular weight by Western-blot: 60kd
-
Tested applications
ELISA, WB, IHC, IP
-
Species reactivity
Human,Mouse,Rat; other species not tested.
-
Alternative names
Heat shOCk 70 kDa protein 13 antibody; HSPA13 antibody; STCH antibody
-
Isotype
Rabbit IgG
-
Preparation
This antibody was obtained by immunization of HSPA13 recombinant protein (Accession Number: NM_006948). Purification method: Antigen affinity purified.
-
Clonality
Polyclonal
-
Formulation
PBS with 0.1% sodium azide and 50% glycerol pH 7.3.
-
Storage instructions
Store at -20℃. DO NOT ALIQUOT
-
Applications
Recommended Dilution:
WB: 1:500-1:5000
IP: 1:200-1:1000
IHC: 1:20-1:200
-
Validations

human brain tissue were subjected to SDS PAGE followed by western blot with Catalog No:111572(HSPA13 antibody) at dilution of 1:500
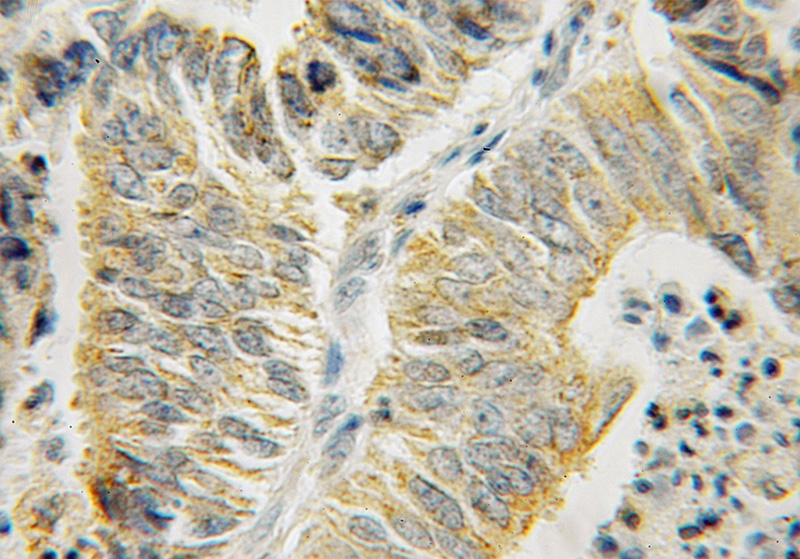
Immunohistochemical of paraffin-embedded human endometrial cancer using Catalog No:111572(HSPA13 antibody) at dilution of 1:50 (under 10x lens)

IP Result of anti-HSPA13 (IP:Catalog No:111572, 4ug; Detection:Catalog No:111572 1:300) with HeLa cells lysate 1200ug.
-
Background
HSPA13 (Heat shock 70 kDa protein 13), also known as STCH (the stress 70 protein chaperone), is a member of the Hsp70 family of ATPase “stress” or “heat shock” proteins. Human STCH encodes a 60 kDa protein that is highly enriched in the ER. Recently it has been reported that overexpression of the HSPA13 gene reduces prion disease incubation time in mice.
-
References
- Grizenkova J, Akhtar S, Hummerich H. Overexpression of the Hspa13 (Stch) gene reduces prion disease incubation time in mice. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 109(34):13722-7. 2012.
Related Products / Services
Please note: All products are "FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY AND ARE NOT INTENDED FOR DIAGNOSTIC OR THERAPEUTIC USE"
