-
Product Name
HORMAD1 antibody
- Documents
-
Description
HORMAD1 Rabbit Polyclonal antibody. Positive IP detected in mouse testis tissue. Positive WB detected in mouse testis tissue. Observed molecular weight by Western-blot: 45 kDa
-
Tested applications
ELISA, WB, IP
-
Species reactivity
Human,Mouse,Rat; other species not tested.
-
Alternative names
Cancer/testis antigen 46 antibody; CT46 antibody; DKFZp434A1315 antibody; HORMA domain containing 1 antibody; HORMAD1 antibody; Newborn ovary HORMA protein antibody; NOHMA antibody; RP11 363I22.1 antibody
-
Isotype
Rabbit IgG
-
Preparation
This antibody was obtained by immunization of HORMAD1 recombinant protein (Accession Number: XM_047431808). Purification method: Antigen affinity purified.
-
Clonality
Polyclonal
-
Formulation
PBS with 0.02% sodium azide and 50% glycerol pH 7.3.
-
Storage instructions
Store at -20℃. DO NOT ALIQUOT
-
Applications
Recommended Dilution:
WB: 1:500-1:5000
IP: 1:200-1:2000
-
Validations
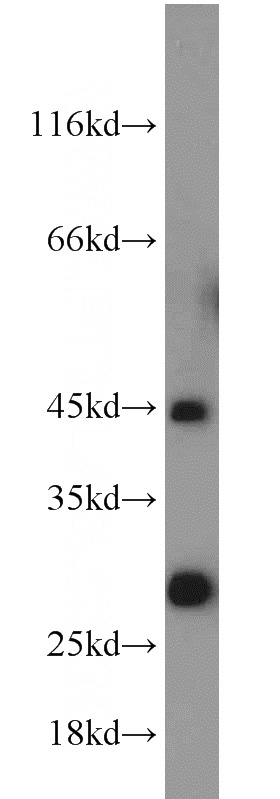
mouse testis tissue were subjected to SDS PAGE followed by western blot with Catalog No:111525(HORMAD1 antibody) at dilution of 1:1000
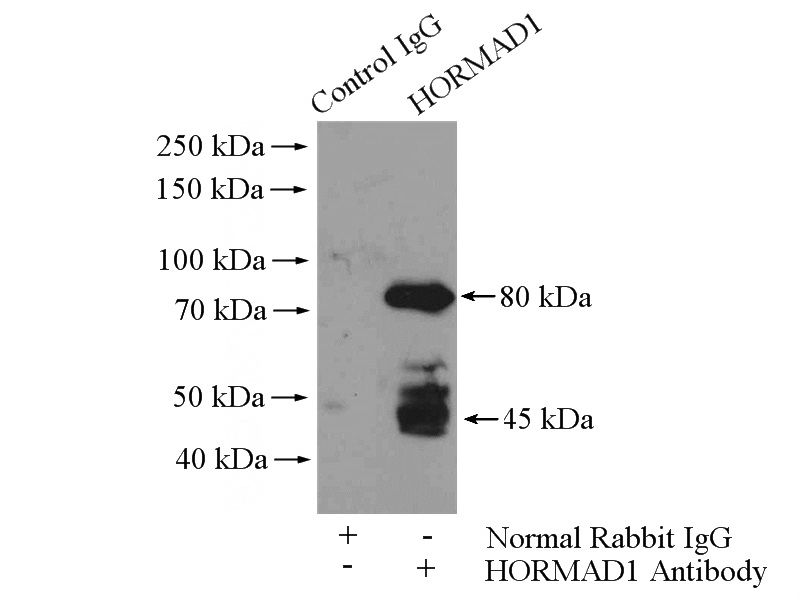
IP Result of anti-HORMAD1 (IP:Catalog No:111525, 4ug; Detection:Catalog No:111525 1:500) with mouse testis tissue lysate 4000ug.
-
Background
HORMA domain-containing proteins regulate interactions between homologous chromosomes (homologs) during meiosis in a wide range of eukaryotes [PMID:21079677]. They also implicated in other processes related to crossover formation, including DSB formation, inhibition of promiscuous formation of the synaptonemal complex (SC), and the meiotic prophase checkpoint that monitors both DSB processing and SCs [PMID:19851446]. HORMAD1 first accumulates on the chromosomes during the leptotene to zygotene stages of meiotic prophase I. As germ cells progress into the pachytene stage, HORMAD1 disappears from the synapsed chromosomal regions. However, once the chromosomes desynapse during the diplotene stage, HORMAD1 again accumulates on the chromosome axis of the desynapsed homologs [PMID:19686734].
-
References
- Fukuda T, Pratto F, Schimenti JC, Turner JM, Camerini-Otero RD, Höög C. Phosphorylation of chromosome core components may serve as axis marks for the status of chromosomal events during mammalian meiosis. PLoS genetics. 8(2):e1002485. 2012.
- Awe JP, Gschweng EH, Vega-Crespo A. Putative immunogenicity expression profiling using human pluripotent stem cells and derivatives. Stem cells translational medicine. 4(2):136-45. 2015.
Related Products / Services
Please note: All products are "FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY AND ARE NOT INTENDED FOR DIAGNOSTIC OR THERAPEUTIC USE"
