-
Product Name
HLA-G Polyclonal Antibody
- Documents
-
Description
Polyclonal antibody to HLA-G
-
Tested applications
WB
-
Species reactivity
Human, Mouse, Rat
-
Alternative names
HLA-G antibody; MHC-G antibody; major histocompatibility complex, class I, G antibody
-
Isotype
Rabbit IgG
-
Preparation
Antigen: Recombinant fusion protein containing a sequence corresponding to amino acids 20-230 of human HLA-G (NP_002118.1).
-
Clonality
Polyclonal
-
Formulation
PBS with 0.02% sodium azide, 50% glycerol, pH7.3.
-
Storage instructions
Store at -20℃. Avoid freeze / thaw cycles.
-
Applications
WB 1:500 - 1:2000
-
Validations
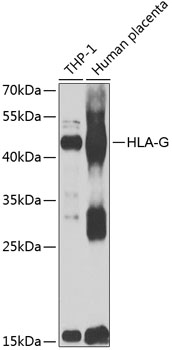
Western blot - HLA-G Polyclonal Antibody
Western blot analysis of extracts of various cell lines, using HLA-G antibody at 1:1000 dilution.Secondary antibody: HRP Goat Anti-Rabbit IgG (H+L) at 1:10000 dilution.Lysates/proteins: 25ug per lane.Blocking buffer: 3% nonfat dry milk in TBST.Detection: ECL Enhanced Kit .Exposure time: 30s.
-
Background
Isoform 1: Non-classical major histocompatibility class Ib molecule involved in immune regulatory processes at the maternal-fetal interface. In complex with B2M/beta-2 microglobulin binds a limited repertoire of nonamer self-peptides derived from intracellular proteins including histones and ribosomal proteins. Peptide-bound HLA-G-B2M complex acts as a ligand for inhibitory/activating KIR2DL4, LILRB1 and LILRB2 receptors on uterine immune cells to promote fetal development while maintaining maternal-fetal tolerance. Upon interaction with KIR2DL4 and LILRB1 receptors on decidual NK cells, it triggers NK cell senescence-associated secretory phenotype as a molecular switch to promote vascular remodeling and fetal growth in early pregnancy. Through interaction with KIR2DL4 receptor on decidual macrophages induces proinflammatory cytokine production mainly associated with tissue remodeling. Through interaction with LILRB2 receptor triggers differentiation of type 1 regulatory T cells and myeloid-derived suppressor cells, both of which actively maintain maternal-fetal tolerance. May play a role in balancing tolerance and antiviral-immunity at maternal-fetal interface by keeping in check the effector functions of NK, CD8+ T cells and B cells. Reprograms B cells toward an immune suppressive phenotype via LILRB1. May induce immune activation/suppression via intercellular membrane transfer (trogocytosis), likely enabling interaction with KIR2DL4, which resides mostly in endosomes. Through interaction with the inhibitory receptor CD160 on endothelial cells may control angiogenesis in immune privileged sites.; Isoform 2: Likely does not bind B2M and presents peptides. Negatively regulates NK cell- and CD8+ T cell-mediated cytotoxicity.; Isoform 3: Likely does not bind B2M and presents peptides. Negatively regulates NK cell- and CD8+ T cell-mediated cytotoxicity.; Isoform 4: Likely does not bind B2M and presents peptides. Negatively regulates NK cell- and CD8+ T cell-mediated cytotoxicity.; Isoform 5: Non-classical major histocompatibility class Ib molecule involved in immune regulatory processes at the maternal-fetal interface. In complex with B2M/beta-2 microglobulin binds a limited repertoire of nonamer self-peptides derived from intracellular proteins including histones and ribosomal proteins. Peptide-bound HLA-G-B2M complex acts as a ligand for inhibitory/activating KIR2DL4, LILRB1 and LILRB2 receptors on uterine immune cells to promote fetal development while maintaining maternal-fetal tolerance. Upon interaction with KIR2DL4 and LILRB1 receptors on decidual NK cells, it triggers NK cell senescence-associated secretory phenotype as a molecular switch to promote vascular remodeling and fetal growth in early pregnancy. Through interaction with KIR2DL4 receptor on decidual macrophages induces proinflammatory cytokine production mainly associated with tissue remodeling. Through interaction with LILRB2 receptor triggers differentiation of type 1 regulatory T cells and myeloid-derived suppressor cells, both of which actively maintain maternal-fetal tolerance. Reprograms B cells toward an immune suppressive phenotype via LILRB1.; Isoform 6: Likely does not bind B2M and presents peptides.; Isoform 7: Likely does not bind B2M and presents peptides.
Related Products / Services
Please note: All products are "FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY AND ARE NOT INTENDED FOR DIAGNOSTIC OR THERAPEUTIC USE"
