-
Product Name
GABBR2 Polyclonal Antibody
- Documents
-
Description
Polyclonal antibody to GABBR2
-
Tested applications
WB
-
Species reactivity
Human, Mouse, Rat
-
Alternative names
GABBR2 antibody; GABABR2 antibody; GPR51 antibody; GPRC3B antibody; HG20 antibody; HRIHFB2099 antibody; gamma-aminobutyric acid type B receptor subunit 2 antibody
-
Isotype
Rabbit IgG
-
Preparation
Antigen: Recombinant fusion protein containing a sequence corresponding to amino acids 60-310 of human GABBR2 (NP_005449.5).
-
Clonality
Polyclonal
-
Formulation
PBS with 0.02% sodium azide, 50% glycerol, pH7.3.
-
Storage instructions
Store at -20℃. Avoid freeze / thaw cycles.
-
Applications
WB 1:500 - 1:2000
-
Validations
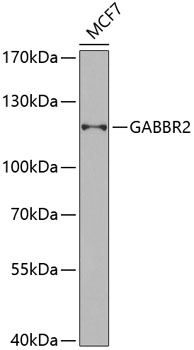
Western blot - GABBR2 Polyclonal Antibody
Western blot analysis of extracts of MCF-7 cells, using GABBR2 antibody at 1:1000 dilution.Secondary antibody: HRP Goat Anti-Rabbit IgG (H+L) at 1:10000 dilution.Lysates/proteins: 25ug per lane.Blocking buffer: 3% nonfat dry milk in TBST.Detection: ECL Basic Kit .Exposure time: 120s.
-
Background
Component of a heterodimeric G-protein coupled receptor for GABA, formed by GABBR1 and GABBR2. Within the heterodimeric GABA receptor, only GABBR1 seems to bind agonists, while GABBR2 mediates coupling to G proteins. Ligand binding causes a conformation change that triggers signaling via guanine nucleotide-binding proteins (G proteins) and modulates the activity of down-stream effectors, such as adenylate cyclase. Signaling inhibits adenylate cyclase, stimulates phospholipase A2, activates potassium channels, inactivates voltage-dependent calcium-channels and modulates inositol phospholipid hydrolysis. Plays a critical role in the fine-tuning of inhibitory synaptic transmission. Pre-synaptic GABA receptor inhibits neurotransmitter release by down-regulating high-voltage activated calcium channels, whereas postsynaptic GABA receptor decreases neuronal excitability by activating a prominent inwardly rectifying potassium (Kir) conductance that underlies the late inhibitory postsynaptic potentials. Not only implicated in synaptic inhibition but also in hippocampal long-term potentiation, slow wave sleep, muscle relaxation and antinociception (Probable).
Related Products / Services
Please note: All products are "FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY AND ARE NOT INTENDED FOR DIAGNOSTIC OR THERAPEUTIC USE"
