-
Product Name
G-CSFR antibody
- Documents
-
Description
G-CSFR Rabbit Polyclonal antibody. Positive WB detected in human placenta tissue. Observed molecular weight by Western-blot: 85kd
-
Tested applications
ELISA, WB
-
Species reactivity
Human; other species not tested.
-
Alternative names
CD114 antibody; CSF3R antibody; G CSF R antibody; G CSF receptor antibody; GCSFR antibody; G-CSFR antibody
-
Isotype
Rabbit IgG
-
Preparation
This antibody was obtained by immunization of Peptide (Accession Number: NM_000760). Purification method: Antigen affinity purified.
-
Clonality
Polyclonal
-
Formulation
PBS with 0.02% sodium azide and 50% glycerol pH 7.3.
-
Storage instructions
Store at -20℃. DO NOT ALIQUOT
-
Applications
Recommended Dilution:
WB: 1:500-1:5000
-
Validations
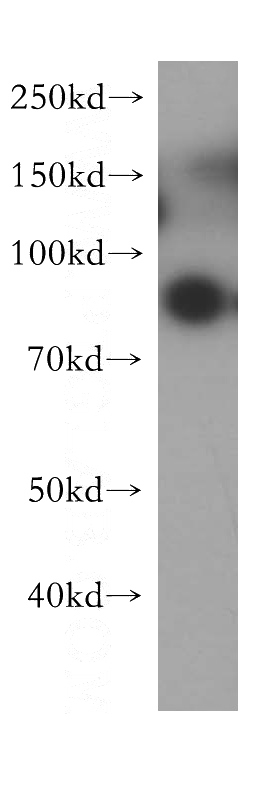
human placenta tissue were subjected to SDS PAGE followed by western blot with Catalog No:110917(G-CSF-R antibody) at dilution of 1:300
-
Background
G-CSF-R, also named as CSF3R, CD114 and GCSFR is the receptor for colony stimulating factor 3, a cytokine that controls the production, differentiation, and function of granulocytes. It is a 130 kD to 150 kD glycoprotein single chain receptor which binds and activated by GCSF. In addition it may function in some adhesion or recognition events at the cell surface. It has been classified as a member of the hematopoietic (cytokine) receptor family, cytokine receptor class I, or the gp 130 related cytokine receptor family (although it does not apparently bind to gp 130). GCSF receptors can be found on neutrophils, myeloid leukemia cells that respond to GCSF, bone marrow cells of neutrophilic granulocyte lineage, and on placental trophoblasts. In addition, a soluble form is also expressed. Mutations in this gene are a cause of Kostmann syndrome, also known as severe congenital neutropenia.
Related Products / Services
Please note: All products are "FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY AND ARE NOT INTENDED FOR DIAGNOSTIC OR THERAPEUTIC USE"
