-
Product Name
RSV RSV-F / Fusion Glycoprotein (His Tag)
- Documents
-
Description
During virus entry, induces fusion of viral and cellular membranes leading to delivery of the nucleocapsid into the cytoplasm. The fusogenic activity is inactive untill entry into host cell endosome, where a furin-like protease cleaves off a small peptide between F1 and F2. Interacts directly with heparan sulfate and may participates in virus attachment. Furthermore, the F2 subunit was identifed as the major determinant of RSV host cell specificity. Later in infection, proteins F expressed at the plasma membrane of infected cells can mediate fusion with adjacent cells to form syncytia, a cytopathic effect that could lead to tissue necrosis. The fusion protein is also able to trigger p53-dependent apoptosis.
-
Protein name
Fusion glycoprotein F0
-
Protein short names
F; PROTEIN F; FUSION PROTEIN (F); RESPIRATORY SYNCYTIAL VIRUS; RSVGP08
-
Uniprot ID
P11209
-
Gene Name
F
-
Source/Expression Host
Baculovirus-Insect Cells
-
Expression Plasmid/cDNA
A DNA sequence encoding the extracellular domain of human RSV (strain RSS-2) fusion protein (P11209) (Met 1-Thr 529) was expressed with a polyhistidine tag at the C-terminus.
-
Protein Species
RSV
-
Molecular weight
The secreted recombinant human RSV (strain RSS-2) comprises 519 amino acids with a predicted molecular mass of 57.8 kDa. The RSV F0 precursor protein is cleaved into the disulfide-linked F1 and F2 subunits. As a result of glycosylation, the apparent molecular mass of the protein is approximately 63 kDa and 44-53 KDa in SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions, corresponding to the two subunits respectively.
-
Purity
> 95 % as determined by SDS-PAGE
-
Validations
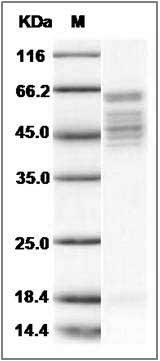
Human RSV Fusion protein / RSV-F (Strain RSS-2) Protein (His Tag) SDS-PAGE
Related Products / Services
Please note: All products are "FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY AND ARE NOT INTENDED FOR DIAGNOSTIC OR THERAPEUTIC USE"
