-
Product Name
ELN antibody
- Documents
-
Description
ELN Rabbit Polyclonal antibody. Positive IHC detected in mouse lung tissue.
-
Tested applications
ELISA, IHC
-
Species reactivity
Human; other species not tested.
-
Alternative names
desmosine antibody; elastin antibody; ELN antibody; FLJ38671 antibody; FLJ43523 antibody; SVAS antibody; Tropoelastin antibody; WBS antibody
-
Isotype
Rabbit IgG
-
Preparation
This antibody was obtained by immunization of ELN recombinant protein (Accession Number: NM_001278916). Purification method: Antigen affinity purified.
-
Clonality
Polyclonal
-
Formulation
PBS with 0.1% sodium azide and 50% glycerol pH 7.3.
-
Storage instructions
Store at -20℃. DO NOT ALIQUOT
-
Applications
Recommended Dilution:
IHC: 1:20-1:200
-
Validations
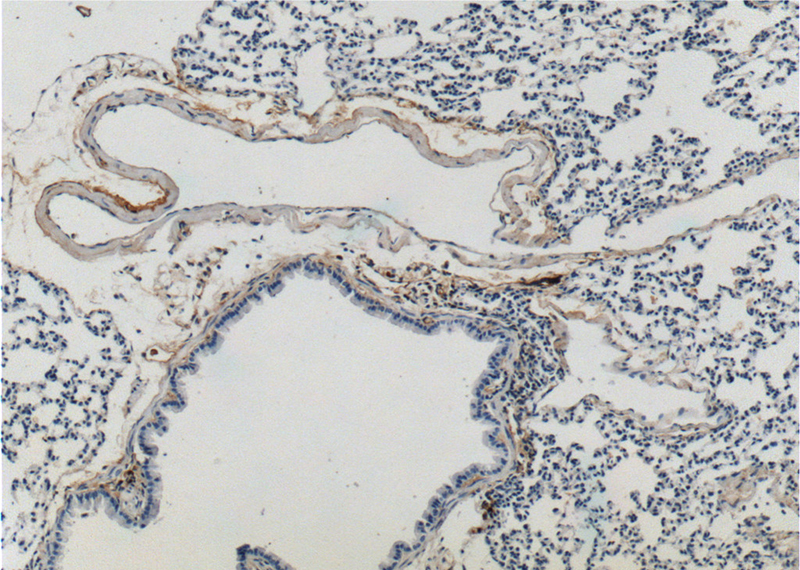
Immunohistochemistry of paraffin-embedded mouse lung tissue slide using Catalog No:110285(ELN Antibody) at dilution of 1:200 (under 10x lens).
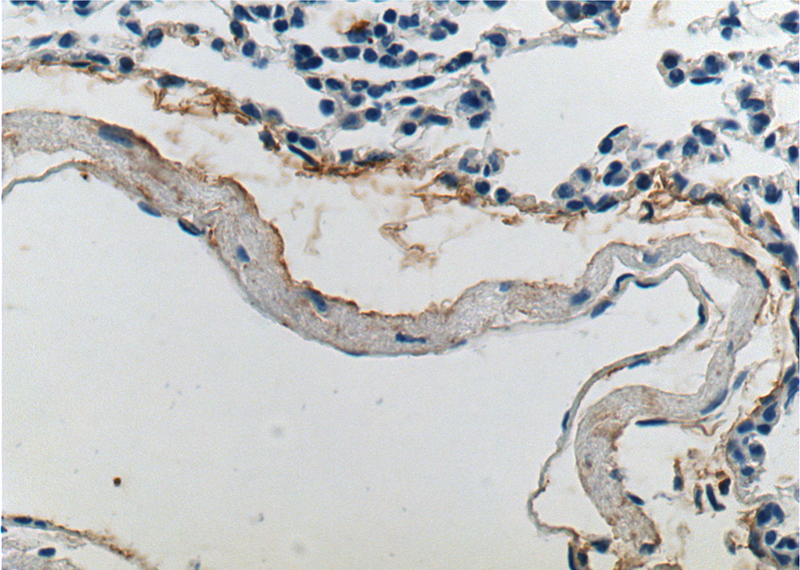
Immunohistochemistry of paraffin-embedded mouse lung tissue slide using Catalog No:110285(ELN Antibody) at dilution of 1:200 (under 40x lens).
-
Background
Elastic fibers are an abundant and integral part of many extracellular matrices, in which they provide the elastic properties to tissues such as arterial, lung, and skin. Elastic fibers are consisting of an elastin core surrounded by a mantle of fibrillin-rich microfibrils (PMID: 12082143). Elastin is an extremely durable, insoluble biopolymer formed through the lysine-mediated crosslinking of its soluble precursor tropoelastin, which is an approximately 60-70 kDa protein (PMID: 15837523). Deletions and mutations in the elastin gene (ELN) are associated with supravalvular aortic stenosis (SVAS) and autosomal dominant cutis laxa.
-
References
- Chuang TD, Pearce WJ, Khorram O. miR-29c induction contributes to downregulation of vascular extracellular matrix proteins by glucocorticoids. American journal of physiology. Cell physiology. 309(2):C117-25. 2015.
- Khorram O, Chuang TD, Pearce WJ. Long-term effects of maternal undernutrition on offspring carotid artery remodeling: role of miR-29c. Journal of developmental origins of health and disease. 6(4):342-9. 2015.
Related Products / Services
Please note: All products are "FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY AND ARE NOT INTENDED FOR DIAGNOSTIC OR THERAPEUTIC USE"
