-
Product Name
EIF3E Polyclonal Antibody
- Documents
-
Description
Polyclonal antibody to EIF3E
-
Tested applications
WB, IF
-
Species reactivity
Human, Mouse
-
Alternative names
EIF3E antibody; EIF3-P48 antibody; EIF3S6 antibody; INT6 antibody; eIF3-p46 antibody; eukaryotic translation initiation factor 3 subunit E antibody
-
Isotype
Rabbit IgG
-
Preparation
Antigen: Recombinant fusion protein containing a sequence corresponding to amino acids 1-445 of human EIF3E (NP_001559.1).
-
Clonality
Polyclonal
-
Formulation
PBS with 0.02% sodium azide, 50% glycerol, pH7.3.
-
Storage instructions
Store at -20℃. Avoid freeze / thaw cycles.
-
Applications
WB 1:500 - 1:2000
IF 1:50 - 1:100 -
Validations
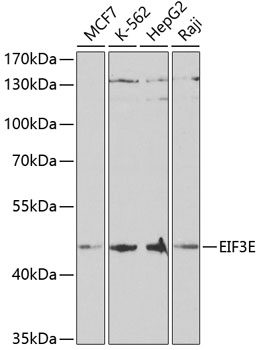
Western blot - EIF3E Polyclonal Antibody
Western blot analysis of extracts of various cell lines, using EIF3E antibody at 1:1000 dilution.Secondary antibody: HRP Goat Anti-Rabbit IgG (H+L) at 1:10000 dilution.Lysates/proteins: 25ug per lane.Blocking buffer: 3% nonfat dry milk in TBST.Detection: ECL Basic Kit .Exposure time: 90s.
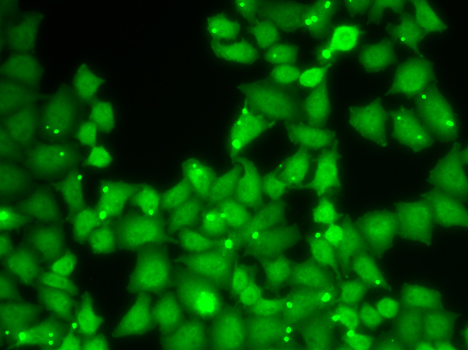
Immunofluorescence - EIF3E Polyclonal Antibody
Immunofluorescence analysis of HeLa cells using EIF3E antibody .
-
Background
Component of the eukaryotic translation initiation factor 3 (eIF-3) complex, which is required for several steps in the initiation of protein synthesis. The eIF-3 complex associates with the 40S ribosome and facilitates the recruitment of eIF-1, eIF-1A, eIF-2:GTP:methionyl-tRNAi and eIF-5 to form the 43S pre-initiation complex (43S PIC). The eIF-3 complex stimulates mRNA recruitment to the 43S PIC and scanning of the mRNA for AUG recognition. The eIF-3 complex is also required for disassembly and recycling of post-termination ribosomal complexes and subsequently prevents premature joining of the 40S and 60S ribosomal subunits prior to initiation. The eIF-3 complex specifically targets and initiates translation of a subset of mRNAs involved in cell proliferation, including cell cycling, differentiation and apoptosis, and uses different modes of RNA stem-loop binding to exert either translational activation or repression. Required for nonsense-mediated mRNA decay (NMD); may act in conjunction with UPF2 to divert mRNAs from translation to the NMD pathway. May interact with MCM7 and EPAS1 and regulate the proteasome-mediated degradation of these proteins.
Related Products / Services
Please note: All products are "FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY AND ARE NOT INTENDED FOR DIAGNOSTIC OR THERAPEUTIC USE"
