-
Product Name
Mouse ENTPD5 (His Tag) recombinant protein
- Documents
-
Description
Uridine diphosphatase (UDPase) that promotes protein N-glycosylation and ATP level regulation. UDP hydrolysis promotes protein N-glycosylation and folding in the endoplasmic reticulum, as well as elevated ATP consumption in the cytosol via an ATP hydrolysis cycle. Together with CMPK1 and AK1, constitutes an ATP hydrolysis cycle that converts ATP to AMP and results in a compensatory increase in aerobic glycolysis. The nucleotide hydrolyzing preference is GDP > IDP > UDP, but not any other nucleoside di-, mono- or triphosphates, nor thiamine pyrophosphate. Plays a key role in the AKT1-PTEN signaling pathway by promoting glycolysis in proliferating cells in response to phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K) signaling.
-
Protein name
Ectonucleoside triphosphate diphosphohydrolase 5
-
Protein short names
ER-UDPASE; PROTO-ONCOGENE CPH; PCPH; NUCLEOSIDE DIPHOSPHATASE; GDPASE ENTPD5; CD39L4; URIDINE-DIPHOSPHATASE ENTPD5; GUANOSINE-DIPHOSPHATASE ENTPD5; CD39 ANTIGEN-LIKE 4; AI196558; NTPDASE-5; UDPASE ENTPD5; NTPDASE5; PCPH PROTO-ONCOGENE PROTEIN; AI987697; NTPDASE 5; CD39-LIKE 4; MNTPASE
-
Uniprot ID
Q9WUZ9
-
Gene Name
Entpd5; Cd39l4
-
Source/Expression Host
Baculovirus-Insect Cells
-
Expression Plasmid/cDNA
A DNA sequence encoding the mouse ENTPD5 (Q9WUZ9) (Thr19-Ser427) was fused with a polyhistidine tag at the C-terminus.
-
Protein Species
Mouse
-
Molecular weight
The recombinant mouse ENTPD5 consists of 419 amino acids and has a calculated molecular mass of 46.6 kDa. The recombinant protein migrates as an approximately 45 kDa band in SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions.
-
Purity
> 90 % as determined by SDS-PAGE
-
Activity
Measured by its ability to hydrolyze the 5’phosphate groups from the substrate guanosine5’diphosphate (GDP).
The specific activity is > 15000 pmols/min/μg. -
Validations
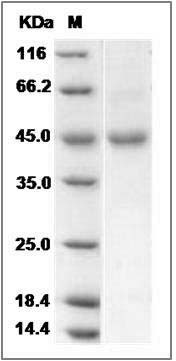
Mouse ENTPD5 Protein (His Tag) SDS-PAGE
Related Products / Services
Please note: All products are "FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY AND ARE NOT INTENDED FOR DIAGNOSTIC OR THERAPEUTIC USE"
