-
Product Name
DTL Polyclonal Antibody
- Documents
-
Description
Polyclonal antibody to DTL
-
Tested applications
WB
-
Species reactivity
Mouse, Rat
-
Alternative names
DTL antibody; CDT2 antibody; DCAF2 antibody; L2DTL antibody; RAMP antibody; denticleless protein homolog antibody
-
Isotype
Rabbit IgG
-
Preparation
Antigen: Recombinant fusion protein containing a sequence corresponding to amino acids 541-730 of human DTL (NP_057532.3).
-
Clonality
Polyclonal
-
Formulation
PBS with 0.02% sodium azide, 50% glycerol, pH7.3.
-
Storage instructions
Store at -20℃. Avoid freeze / thaw cycles.
-
Applications
WB 1:500 - 1:2000
-
Validations
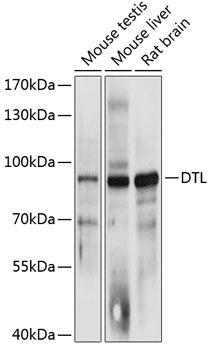
Western blot - DTL Polyclonal Antibody
Western blot analysis of extracts of various cell lines, using DTL antibody at 1:3000 dilution.Secondary antibody: HRP Goat Anti-Rabbit IgG (H+L) at 1:10000 dilution.Lysates/proteins: 25ug per lane.Blocking buffer: 3% nonfat dry milk in TBST.Detection: ECL Basic Kit .Exposure time: 1s.
-
Background
Substrate-specific adapter of a DCX (DDB1-CUL4-X-box) E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase complex required for cell cycle control, DNA damage response and translesion DNA synthesis. The DCX(DTL) complex, also named CRL4(CDT2) complex, mediates the polyubiquitination and subsequent degradation of CDT1, CDKN1A/p21(CIP1), FBH1, KMT5A and SDE2. CDT1 degradation in response to DNA damage is necessary to ensure proper cell cycle regulation of DNA replication. CDKN1A/p21(CIP1) degradation during S phase or following UV irradiation is essential to control replication licensing. KMT5A degradation is also important for a proper regulation of mechanisms such as TGF-beta signaling, cell cycle progression, DNA repair and cell migration. Most substrates require their interaction with PCNA for their polyubiquitination: substrates interact with PCNA via their PIP-box, and those containing the 'K+4' motif in the PIP box, recruit the DCX(DTL) complex, leading to their degradation. In undamaged proliferating cells, the DCX(DTL) complex also promotes the 'Lys-164' monoubiquitination of PCNA, thereby being involved in PCNA-dependent translesion DNA synthesis.
Related Products / Services
Please note: All products are "FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY AND ARE NOT INTENDED FOR DIAGNOSTIC OR THERAPEUTIC USE"
