-
Product Name
CPS1 antibody
- Documents
-
Description
CPS1 Rabbit Polyclonal antibody. Positive IF detected in HepG2 cells. Positive WB detected in HepG2 cells, mouse liver tissue. Observed molecular weight by Western-blot: 116 kDa,165 kDa
-
Tested applications
ELISA, IF, WB
-
Species reactivity
Human,Mouse,Rat; other species not tested.
-
Alternative names
CPS1 antibody; CPSase I antibody
-
Isotype
Rabbit IgG
-
Preparation
This antibody was obtained by immunization of Peptide (Accession Number: XM_011510641). Purification method: Antigen affinity purified.
-
Clonality
Polyclonal
-
Formulation
PBS with 0.02% sodium azide and 50% glycerol pH 7.3.
-
Storage instructions
Store at -20℃. DO NOT ALIQUOT
-
Applications
Recommended Dilution:
WB: 1:500-1:5000
IF: 1:10-1:100
-
Validations
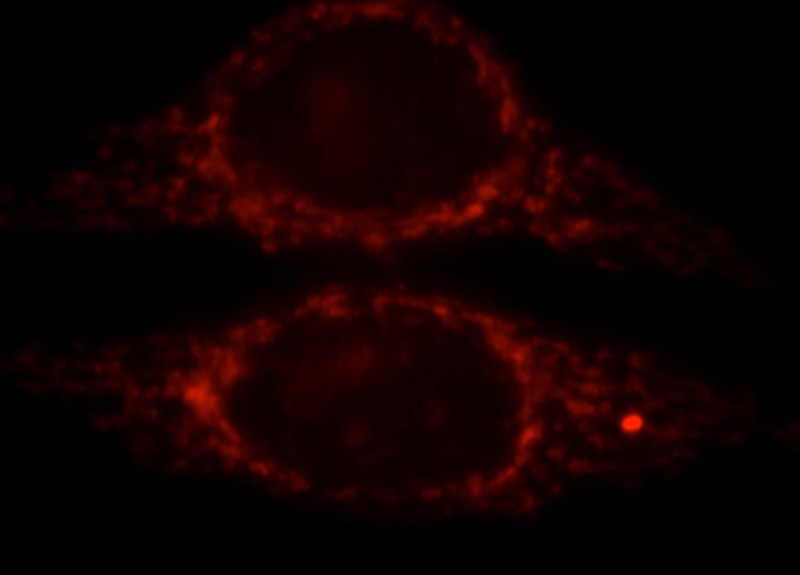
Immunofluorescent analysis of HepG2 cells, using CPS1 antibody Catalog No:109522 at 1:25 dilution and Rhodamine-labeled goat anti-rabbit IgG (red).

HepG2 cells were subjected to SDS PAGE followed by western blot with Catalog No:109522(CPS1 Antibody) at dilution of 1:1000
-
Background
CPS1 is an enzyme that catalyzes the first committed step of the hepatic urea cycle, which is important in the removal of excess urea from cells. Expressed primarily in the liver and small intestine, CPS1 can be used as a marker for mitochondria in these tissues. In addition, CPS1 expression appears to be lost in adenocarcinomas of the small intestine. The antibody can recognize two isoforms of this gene around 165 kDa and 116 kDa.
-
References
- Rodriguez-Suarez E, Mato JM, Elortza F. Proteomics analysis of human nonalcoholic fatty liver. Methods in molecular biology (Clifton, N.J.). 909:241-58. 2012.
- Tummala KS, Gomes AL, Yilmaz M. Inhibition of de novo NAD(+) synthesis by oncogenic URI causes liver tumorigenesis through DNA damage. Cancer cell. 26(6):826-39. 2014.
Related Products / Services
Please note: All products are "FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY AND ARE NOT INTENDED FOR DIAGNOSTIC OR THERAPEUTIC USE"
