-
Product Name
CEBPA Polyclonal Antibody
- Documents
-
Description
Polyclonal antibody to CEBPA
-
Tested applications
WB, IHC
-
Species reactivity
Human, Mouse, Rat
-
Alternative names
CEBPA antibody; C/EBP-alpha antibody; CEBP antibody; CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein alpha antibody
-
Isotype
Rabbit IgG
-
Preparation
Antigen: Recombinant fusion protein containing a sequence corresponding to amino acids 1-205 of human CEBPA (NP_004355.2).
-
Clonality
Polyclonal
-
Formulation
PBS with 0.02% sodium azide, 50% glycerol, pH7.3.
-
Storage instructions
Store at -20℃. Avoid freeze / thaw cycles.
-
Applications
WB 1:500 - 1:2000
IHC 1:50 - 1:200 -
Validations
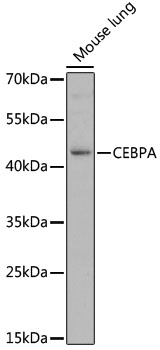
Western blot - CEBPA Polyclonal Antibody
Western blot analysis of extracts of mouse lung, using CEBPA antibody at 1:1000 dilution.Secondary antibody: HRP Goat Anti-Rabbit IgG (H+L) at 1:10000 dilution.Lysates/proteins: 25ug per lane.Blocking buffer: 3% nonfat dry milk in TBST.Detection: ECL Basic Kit .Exposure time: 30s.
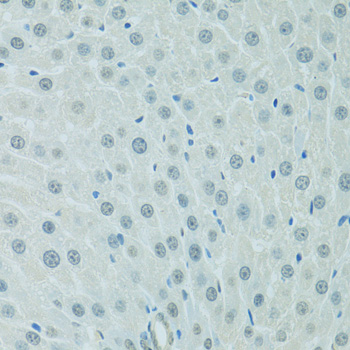
Immunohistochemistry - CEBPA Polyclonal Antibody
Immunohistochemistry of paraffin-embedded rat liver using CEBPA antibody at dilution of 1:100 (40x lens).
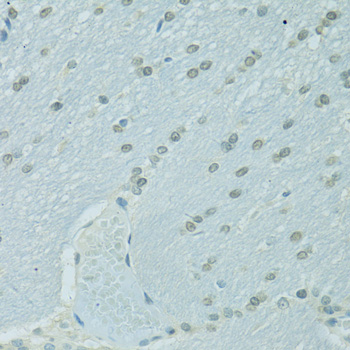
Immunohistochemistry - CEBPA Polyclonal Antibody
Immunohistochemistry of paraffin-embedded rat brain using CEBPA antibody at dilution of 1:100 (40x lens).
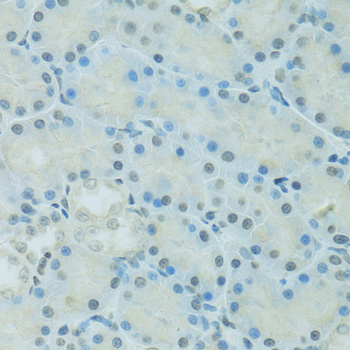
Immunohistochemistry - CEBPA Polyclonal Antibody
Immunohistochemistry of paraffin-embedded rat kidney using CEBPA antibody at dilution of 1:100 (40x lens).
-
Background
Transcription factor that coordinates proliferation arrest and the differentiation of myeloid progenitors, adipocytes, hepatocytes, and cells of the lung and the placenta. Binds directly to the consensus DNA sequence 5'-T[TG]NNGNAA[TG]-3' acting as an activator on distinct target genes. During early embryogenesis, plays essential and redundant functions with CEBPB. Essential for the transition from common myeloid progenitors (CMP) to granulocyte/monocyte progenitors (GMP). Critical for the proper development of the liver and the lung (By similarity). Necessary for terminal adipocyte differentiation, is required for postnatal maintenance of systemic energy homeostasis and lipid storage (By similarity). To regulate these different processes at the proper moment and tissue, interplays with other transcription factors and modulators. Downregulates the expression of genes that maintain cells in an undifferentiated and proliferative state through E2F1 repression, which is critical for its ability to induce adipocyte and granulocyte terminal differentiation. Reciprocally E2F1 blocks adipocyte differentiation by binding to specific promoters and repressing CEBPA binding to its target gene promoters. Proliferation arrest also depends on a functional binding to SWI/SNF complex. In liver, regulates gluconeogenesis and lipogenesis through different mechanisms. To regulate gluconeogenesis, functionally cooperates with FOXO1 binding to IRE-controlled promoters and regulating the expression of target genes such as PCK1 or G6PC. To modulate lipogenesis, interacts and transcriptionally synergizes with SREBF1 in promoter activation of specific lipogenic target genes such as ACAS2. In adipose tissue, seems to act as FOXO1 coactivator accessing to ADIPOQ promoter through FOXO1 binding sites (By similarity).; Isoform 3: Can act as dominant-negative. Binds DNA and have transctivation activity, even if much less efficiently than isoform 2. Does not inhibit cell proliferation.; Isoform 4: Directly and specifically enhances ribosomal DNA transcription interacting with RNA polymerase I-specific cofactors and inducing histone acetylation.
Related Products / Services
Please note: All products are "FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY AND ARE NOT INTENDED FOR DIAGNOSTIC OR THERAPEUTIC USE"
