-
Product Name
CEBPA antibody
- Documents
-
Description
CEBPA Rabbit Polyclonal antibody. Positive WB detected in L02 cells, human liver tissue. Positive IP detected in L02 cells. Observed molecular weight by Western-blot: 43-45 kDa
-
Tested applications
ELISA, WB, IP
-
Species reactivity
Human,Mouse,Rat; other species not tested.
-
Alternative names
C/EBP alpha antibody; CEBP antibody; CEBPA antibody
-
Isotype
Rabbit IgG
-
Preparation
This antibody was obtained by immunization of Peptide (Accession Number: NM_004364). Purification method: Antigen affinity purified.
-
Clonality
Polyclonal
-
Formulation
PBS with 0.02% sodium azide and 50% glycerol pH 7.3.
-
Storage instructions
Store at -20℃. DO NOT ALIQUOT
-
Applications
Recommended Dilution:
WB: 1:200-1:2000
IP: 1:200-1:2000
-
Validations

L02 cells were subjected to SDS PAGE followed by western blot with Catalog No:109245(CEBPA antibody) at dilution of 1:500
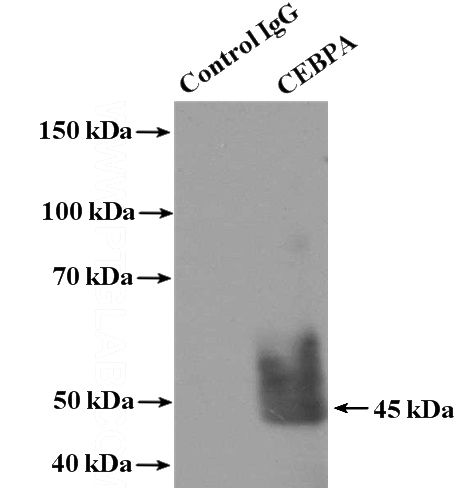
IP Result of anti-CEBPA (IP:Catalog No:109245, 4ug; Detection:Catalog No:109245 1:500) with L02 cells lysate 1800ug.
-
Background
CEBPA and its isoforms play important roles in lineage determination and gene activation in a variety of cell types by activating transcription from lineage-specific promoters. CEBPA is a DNA-binding protein that recognizes two different motifs: the CCAAT homology common to many promoters and the enhanced core homology common to many enhancers. In hematopoiesis, C/EBPa is a key factor in driving the development of myeloid cells interacting with a variety of factors, including c-Myc, PU.1, and microRNAs. It can also form heterodimers with the related proteins CEBP-beta and CEBP-gamma. The encoded protein has been shown to bind to the promoter and modulate the expression of the gene encoding leptin which plays an important role in body weight homeostasis. CEBPA can interact with CDK2 and CDK4, thereby inhibiting these kinases and causing growth arrest in cultured cells. Several pathways have been implicated as the means by which CEBPA mediates cell cycle arrest and proliferation, including p21, cyclin-dependent kinases and the E2F complex via c-Myc.
-
References
- Ding SY, Lee MJ, Summer R, Liu L, Fried SK, Pilch PF. Pleiotropic effects of cavin-1 deficiency on lipid metabolism. The Journal of biological chemistry. 289(12):8473-83. 2014.
- Pan X, Wang P, Luo J. Adipogenic changes of hepatocytes in a high-fat diet-induced fatty liver mice model and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease patients. Endocrine. 48(3):834-47. 2015.
- Lin HS, Gong JN, Su R. miR-199a-5p inhibits monocyte/macrophage differentiation by targeting the activin A type 1B receptor gene and finally reducing C/EBPα expression. Journal of leukocyte biology. 96(6):1023-35. 2014.
- Chen K, He H, Xie Y. miR-125a-3p and miR-483-5p promote adipogenesis via suppressing the RhoA/ROCK1/ERK1/2 pathway in multiple symmetric lipomatosis. Scientific reports. 5:11909. 2015.
- Zhu W, Zou B, Nie R, Zhang Y, Li CM. A-type ECG and EGCG dimers disturb the structure of 3T3-L1 cell membrane and strongly inhibit its differentiation by targeting peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ with miR-27 involved mechanism. The Journal of nutritional biochemistry. 26(11):1124-35. 2015.
Related Products / Services
Please note: All products are "FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY AND ARE NOT INTENDED FOR DIAGNOSTIC OR THERAPEUTIC USE"
