-
Product Name
CDK7 Polyclonal Antibody
- Documents
-
Description
Polyclonal antibody to CDK7
-
Tested applications
WB, IHC, IF
-
Species reactivity
Human, Mouse
-
Alternative names
CDK7 antibody; CAK antibody; CAK1 antibody; CDKN7 antibody; HCAK antibody; MO15 antibody; STK1 antibody; p39MO15 antibody; cyclin-dependent kinase 7 antibody
-
Isotype
Rabbit IgG
-
Preparation
Antigen: Recombinant fusion protein containing a sequence corresponding to amino acids 1-346 of human CDK7 (NP_001790.1).
-
Clonality
Polyclonal
-
Formulation
PBS with 0.02% sodium azide, 50% glycerol, pH7.3.
-
Storage instructions
Store at -20℃. Avoid freeze / thaw cycles.
-
Applications
WB 1:500 - 1:2000
IHC 1:50 - 1:200
IF 1:50 - 1:200 -
Validations
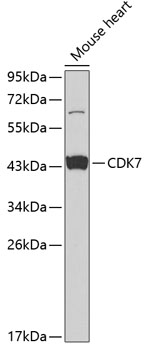
Western blot - CDK7 Polyclonal Antibody
Western blot analysis of extracts of mouse heart, using CDK7 antibody at 1:1000 dilution.Secondary antibody: HRP Goat Anti-Rabbit IgG (H+L) at 1:10000 dilution.Lysates/proteins: 25ug per lane.Blocking buffer: 3% nonfat dry milk in TBST.
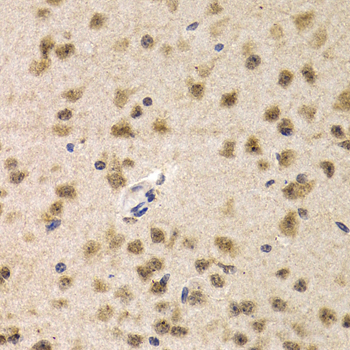
Immunohistochemistry - CDK7 Polyclonal Antibody
Immunohistochemistry of paraffin-embedded mouse brain using CDK7 antibody at dilution of 1:200 (40x lens).
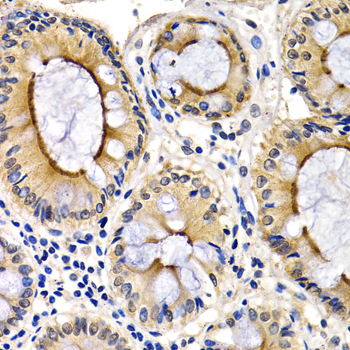
Immunohistochemistry - CDK7 Polyclonal Antibody
Immunohistochemistry of paraffin-embedded human colon using CDK7 antibody at dilution of 1:200 (40x lens).
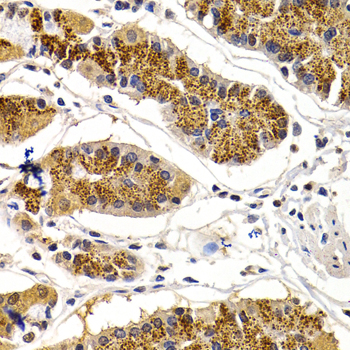
Immunohistochemistry - CDK7 Polyclonal Antibody
Immunohistochemistry of paraffin-embedded human stomach using CDK7 antibody at dilution of 1:200 (40x lens).
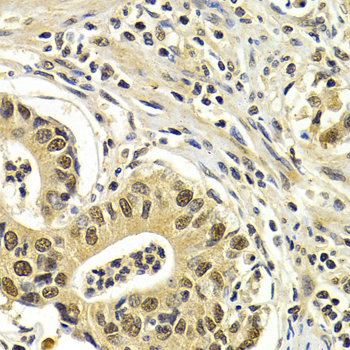
Immunohistochemistry - CDK7 Polyclonal Antibody
Immunohistochemistry of paraffin-embedded human gastric cancer using CDK7 antibody at dilution of 1:200 (40x lens).
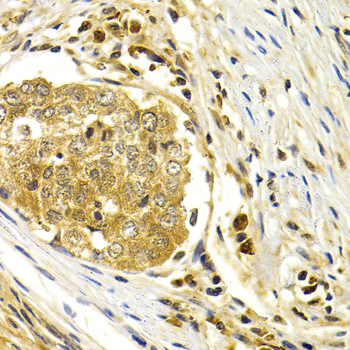
Immunohistochemistry - CDK7 Polyclonal Antibody
Immunohistochemistry of paraffin-embedded human esophageal cancer using CDK7 antibody at dilution of 1:200 (40x lens).
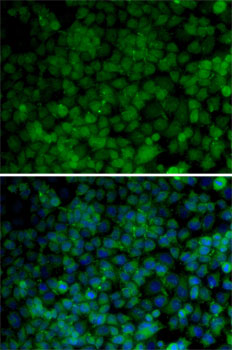
Immunofluorescence - CDK7 Polyclonal Antibody
Immunofluorescence analysis of HeLa cells using CDK7 antibody . Blue: DAPI for nuclear staining.
-
Background
Serine/threonine kinase involved in cell cycle control and in RNA polymerase II-mediated RNA transcription. Cyclin-dependent kinases (CDKs) are activated by the binding to a cyclin and mediate the progression through the cell cycle. Each different complex controls a specific transition between 2 subsequent phases in the cell cycle. Required for both activation and complex formation of CDK1/cyclin-B during G2-M transition, and for activation of CDK2/cyclins during G1-S transition (but not complex formation). CDK7 is the catalytic subunit of the CDK-activating kinase (CAK) complex. Phosphorylates SPT5/SUPT5H, SF1/NR5A1, POLR2A, p53/TP53, CDK1, CDK2, CDK4, CDK6 and CDK11B/CDK11. CAK activates the cyclin-associated kinases CDK1, CDK2, CDK4 and CDK6 by threonine phosphorylation, thus regulating cell cycle progression. CAK complexed to the core-TFIIH basal transcription factor activates RNA polymerase II by serine phosphorylation of the repetitive C-terminal domain (CTD) of its large subunit (POLR2A), allowing its escape from the promoter and elongation of the transcripts. Phosphorylation of POLR2A in complex with DNA promotes transcription initiation by triggering dissociation from DNA. Its expression and activity are constant throughout the cell cycle. Upon DNA damage, triggers p53/TP53 activation by phosphorylation, but is inactivated in turn by p53/TP53; this feedback loop may lead to an arrest of the cell cycle and of the transcription, helping in cell recovery, or to apoptosis. Required for DNA-bound peptides-mediated transcription and cellular growth inhibition.
Related Products / Services
Please note: All products are "FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY AND ARE NOT INTENDED FOR DIAGNOSTIC OR THERAPEUTIC USE"
