-
Product Name
Canine NRG1 recombinant protein
- Documents
-
Description
Neuregulin 1 or NRG1 is one of four proteins in the neuregulin family that act on the EGFR family of receptors. This growth factor was originally identified as a 44-kD glycoprotein that interacts with the NEU / ERBB2 receptor tyrosine kinase to increase its phosphorylation on tyrosine residues. NRG1 is a trophic factor that has been implicated in neural development, neurotransmission, and synaptic plasticity. NRG1 has multiple isoforms that are generated by usage of different promoters and alternative splicing of a single gene. Neuregulin 1 (NRG1) is essential for the development and function of multiple organ systems, and its dysregulation has been linked to diseases such as cancer and schizophrenia. NRG1 is a schizophrenia candidate gene and plays an important role in brain development and neural function. Schizophrenia is a complex disorder, with etiology likely due to epistasis.
-
Protein short names
NRG1-IT2; SMDF; GGFII; HRG; HRG1; MSTP131; GGF; MST131; D230005F13RIK; 6030402G23RIK; GGF2; NDF; HGL; ARIA; HRGA; HRGALPHA
-
Source/Expression Host
Human Cells
-
Expression Plasmid/cDNA
A DNA sequence encoding the canine NRG1 isoform alpha (XP_858147.1) extracellular domain (Ser19-Lys240) was expressed with five amino acids (DDDDK) at the C- terminus.
-
Protein Species
Canine
-
Molecular weight
The recombinant canine NRG1 comprises 228 amino acids and has a predicted molecular mass of 24.7 kDa. The apparent molecular mass of the protein is approximately 47 kDa in SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions due to glycosylation.
-
Purity
> 95 % as determined by SDS-PAGE
-
Activity
Measured by its binding ability in a functional ELISA.
Immobilized canine NRG1 at 10 μg/ml (100 μl/well) can bind human ErbB4-Fc (Cat:502640), The EC50 of human ErbB4-Fc (Cat:502640) is 0.19-0.43 μg/ml. -
Validations
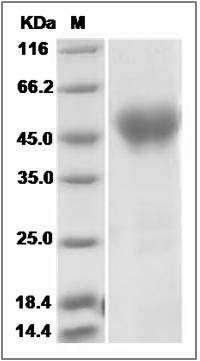
Canine NRG1-alpha Protein () SDS-PAGE
Related Products / Services
Please note: All products are "FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY AND ARE NOT INTENDED FOR DIAGNOSTIC OR THERAPEUTIC USE"
