-
Product Name
ATP6 Polyclonal Antibody
- Documents
-
Description
Polyclonal antibody to ATP6
-
Tested applications
WB, IHC, IF
-
Species reactivity
Human, Mouse, Rat
-
Alternative names
MT-ATP6 antibody; ATPase6 antibody; MTATP6 antibody; ATP6 antibody; mitochondrially encoded ATP synthase 6 antibody
-
Isotype
Rabbit IgG
-
Preparation
Antigen: A synthetic peptide corresponding to a sequence within amino acids 100 to the C-terminus of mouse ATP6 (NP_904333.1).
-
Clonality
Polyclonal
-
Formulation
PBS with 0.02% sodium azide, 50% glycerol, pH7.3.
-
Storage instructions
Store at -20℃. Avoid freeze / thaw cycles.
-
Applications
WB 1:500 - 1:2000
IHC 1:100 - 1:200
IF 1:50 - 1:200 -
Validations
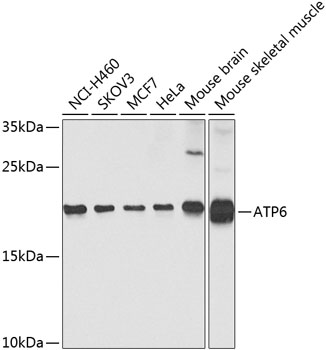
Western blot - ATP6 Polyclonal Antibody
Western blot analysis of extracts of various cell lines, using ATP6 antibody at 1:1000 dilution._Secondary antibody: HRP Goat Anti-Rabbit IgG (H+L) at 1:10000 dilution._Lysates/proteins: 25ug per lane._Blocking buffer: 3% nonfat dry milk in TBST._Detection: ECL Enhanced Kit ._Exposure time: 10s.
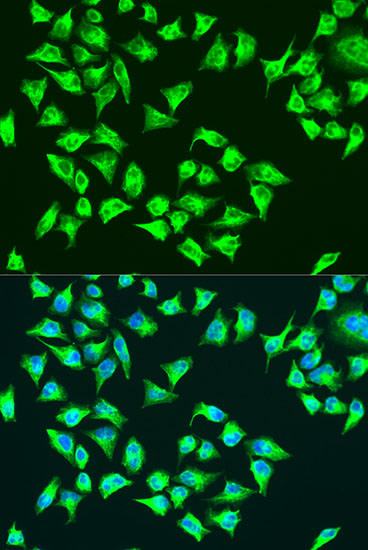
Immunofluorescence - ATP6 Polyclonal Antibody
Immunofluorescence analysis of U2OS cells using ATP6 antibody at dilution of 1:100. Blue: DAPI for nuclear staining.
-
Background
Mitochondrial membrane ATP synthase (F(1)F(0) ATP synthase or Complex V) produces ATP from ADP in the presence of a proton gradient across the membrane which is generated by electron transport complexes of the respiratory chain. F-type ATPases consist of two structural domains, F(1) - containing the extramembraneous catalytic core and F(0) - containing the membrane proton channel, linked together by a central stalk and a peripheral stalk. During catalysis, ATP synthesis in the catalytic domain of F(1) is coupled via a rotary mechanism of the central stalk subunits to proton translocation. Key component of the proton channel; it may play a direct role in the translocation of protons across the membrane.
Related Products / Services
Please note: All products are "FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY AND ARE NOT INTENDED FOR DIAGNOSTIC OR THERAPEUTIC USE"
