-
Product Name
ATP5B Polyclonal Antibody
- Documents
-
Description
Polyclonal antibody to ATP5B
-
Tested applications
WB, IHC, IF
-
Species reactivity
Human, Mouse, Rat
-
Alternative names
ATP5B antibody; ATPMB antibody; ATPSB antibody; HEL-S-271 antibody; ATP synthase subunit beta, mitochondrial antibody
-
Isotype
Rabbit IgG
-
Preparation
Antigen: Recombinant fusion protein containing a sequence corresponding to amino acids 230-529 of human ATP5B (NP_001677.2).
-
Clonality
Polyclonal
-
Formulation
PBS with 0.02% sodium azide, 50% glycerol, pH7.3.
-
Storage instructions
Store at -20℃. Avoid freeze / thaw cycles.
-
Applications
WB 1:500 - 1:2000
IHC 1:50 - 1:200
IF 1:50 - 1:200 -
Validations
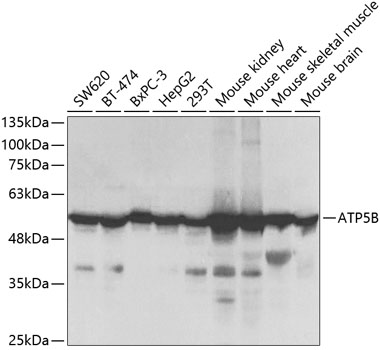
Western blot - ATP5B Polyclonal Antibody
Western blot analysis of extracts of various cell lines, using ATP5B Antibody at 1:1000 dilution.Secondary antibody: HRP Goat Anti-Rabbit IgG (H+L) at 1:10000 dilution.Lysates/proteins: 25ug per lane.Blocking buffer: 3% nonfat dry milk in TBST.Detection: ECL Basic Kit .Exposure time: 3s.
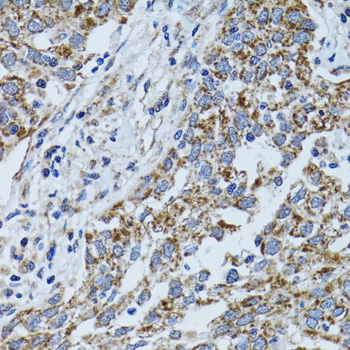
Immunohistochemistry - ATP5B Polyclonal Antibody
Immunohistochemistry of paraffin-embedded human liver injury using ATP5B antibody at dilution of 1:100 (40x lens).
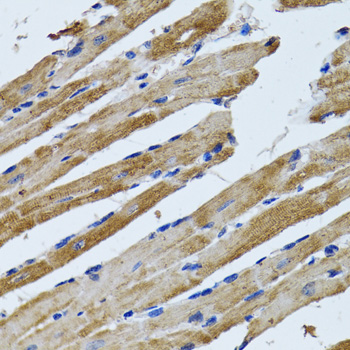
Immunohistochemistry - ATP5B Polyclonal Antibody
Immunohistochemistry of paraffin-embedded rat heart using ATP5B antibody at dilution of 1:100 (40x lens).
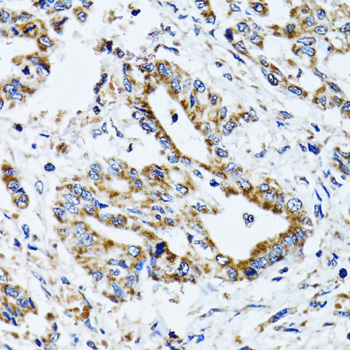
Immunohistochemistry - ATP5B Polyclonal Antibody
Immunohistochemistry of paraffin-embedded human lung cancer using ATP5B antibody at dilution of 1:100 (40x lens).
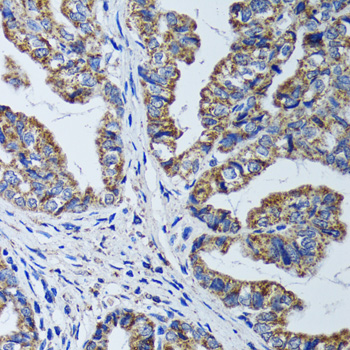
Immunohistochemistry - ATP5B Polyclonal Antibody
Immunohistochemistry of paraffin-embedded human colon carcinoma using ATP5B antibody at dilution of 1:100 (40x lens).
Immunohistochemistry - ATP5B Polyclonal Antibody
Immunohistochemistry of paraffin-embedded human gastric cancer using ATP5B antibody at dilution of 1:100 (40x lens).
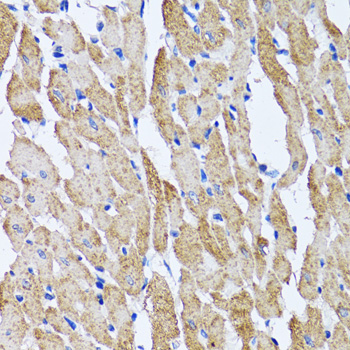
Immunohistochemistry - ATP5B Polyclonal Antibody
Immunohistochemistry of paraffin-embedded mouse heart using ATP5B antibody at dilution of 1:100 (40x lens).
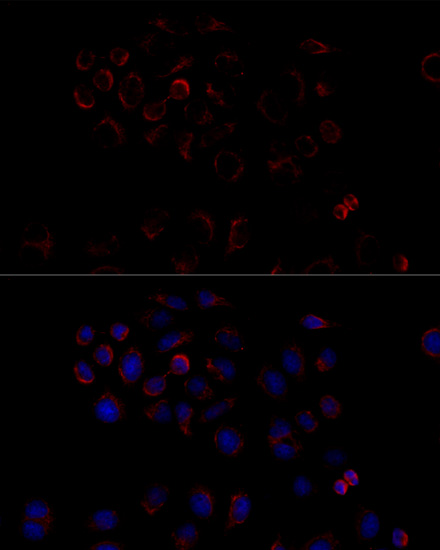
Immunofluorescence - ATP5B Polyclonal Antibody
Immunofluorescence analysis of HeLa cells using ATP5B antibody at dilution of 1:100 (40x lens). Blue: DAPI for nuclear staining.
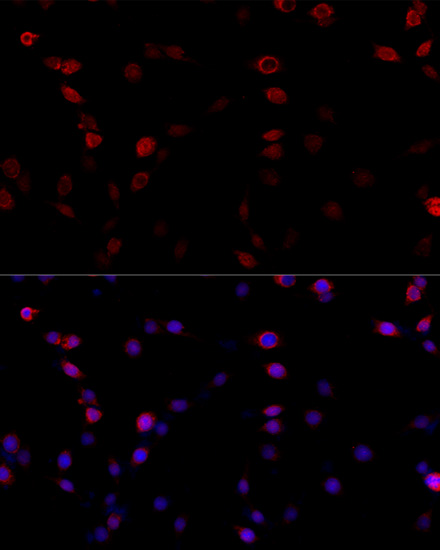
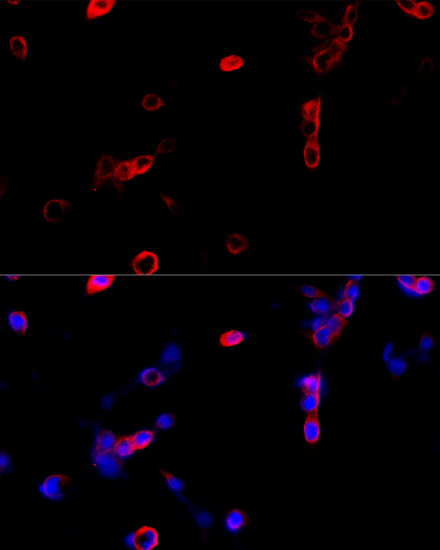
Immunofluorescence - ATP5B Polyclonal Antibody
Immunofluorescence analysis of NIH/3T3 cells using ATP5B antibody at dilution of 1:100 (40x lens). Blue: DAPI for nuclear staining.
-
Background
Mitochondrial membrane ATP synthase (F(1)F(0) ATP synthase or Complex V) produces ATP from ADP in the presence of a proton gradient across the membrane which is generated by electron transport complexes of the respiratory chain. F-type ATPases consist of two structural domains, F(1) - containing the extramembraneous catalytic core, and F(0) - containing the membrane proton channel, linked together by a central stalk and a peripheral stalk. During catalysis, ATP synthesis in the catalytic domain of F(1) is coupled via a rotary mechanism of the central stalk subunits to proton translocation. Subunits alpha and beta form the catalytic core in F(1). Rotation of the central stalk against the surrounding alpha(3)beta(3) subunits leads to hydrolysis of ATP in three separate catalytic sites on the beta subunits.
Related Products / Services
Please note: All products are "FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY AND ARE NOT INTENDED FOR DIAGNOSTIC OR THERAPEUTIC USE"
