-
Product Name
ARCN1 Polyclonal Antibody
- Documents
-
Description
Polyclonal antibody to ARCN1
-
Tested applications
WB
-
Species reactivity
Human, Mouse
-
Alternative names
ARCN1 antibody; COPD antibody; SRMMD antibody; archain 1 antibody
-
Isotype
Rabbit IgG
-
Preparation
Antigen: Recombinant fusion protein containing a sequence corresponding to amino acids 212-511 of human ARCN1 (NP_001646.2).
-
Clonality
Polyclonal
-
Formulation
PBS with 0.02% sodium azide, 50% glycerol, pH7.3.
-
Storage instructions
Store at -20℃. Avoid freeze / thaw cycles.
-
Applications
WB 1:500 - 1:2000
-
Validations
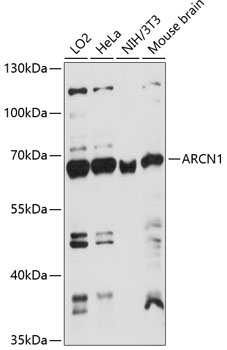
Western blot - ARCN1 Polyclonal Antibody
Western blot analysis of extracts of various cell lines, using ARCN1 antibody at 1:1000 dilution.Secondary antibody: HRP Goat Anti-Rabbit IgG (H+L) at 1:10000 dilution.Lysates/proteins: 25ug per lane.Blocking buffer: 3% nonfat dry milk in TBST.Detection: ECL Basic Kit .Exposure time: 60s.
-
Background
Component of the coatomer, a cytosolic protein complex that binds to dilysine motifs and reversibly associates with Golgi non-clathrin-coated vesicles, which further mediate biosynthetic protein transport from the ER, via the Golgi up to the trans Golgi network. The coatomer complex is required for budding from Golgi membranes, and is essential for the retrograde Golgi-to-ER transport of dilysine-tagged proteins. In mammals, the coatomer can only be recruited by membranes associated to ADP-ribosylation factors (ARFs), which are small GTP-binding proteins; the complex also influences the Golgi structural integrity, as well as the processing, activity, and endocytic recycling of LDL receptors (By similarity).
Related Products / Services
Please note: All products are "FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY AND ARE NOT INTENDED FOR DIAGNOSTIC OR THERAPEUTIC USE"
