-
Product Name
ARC/ARG3.1 antibody
- Documents
-
Description
ARC/ARG3.1 Rabbit Polyclonal antibody. Positive WB detected in SH-SY5Y cells, mouse brain tissue, rat heart tissue. Positive IP detected in mouse brain tissue. Positive IHC detected in human brain tissue. Observed molecular weight by Western-blot: 45-50 kDa
-
Tested applications
ELISA, WB, IHC, IP
-
Species reactivity
Human,Mouse,Rat; other species not tested.
-
Alternative names
ARC antibody; ARC/ARG3.1 antibody; Arg3.1 antibody; KIAA0278 antibody
- Immunogen
-
Isotype
Rabbit IgG
-
Preparation
This antibody was obtained by immunization of ARC/ARG3.1 recombinant protein (Accession Number: XM_047421612). Purification method: Antigen affinity purified.
-
Clonality
Polyclonal
-
Formulation
PBS with 0.02% sodium azide and 50% glycerol pH 7.3.
-
Storage instructions
Store at -20℃. DO NOT ALIQUOT
-
Applications
Recommended Dilution:
WB: 1:500-1:5000
IP: 1:200-1:1000
IHC: 1:20-1:200
-
Validations
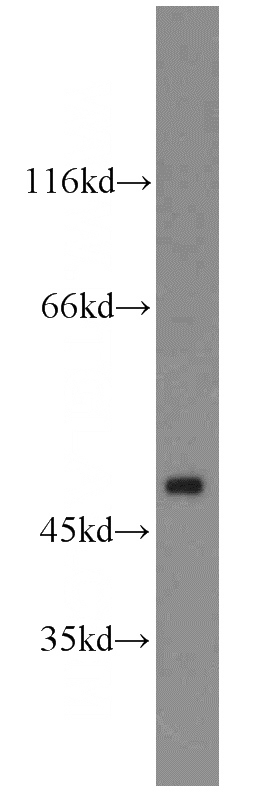
SH-SY5Y cells were subjected to SDS PAGE followed by western blot with Catalog No:108238(ARC antibody) at dilution of 1:500
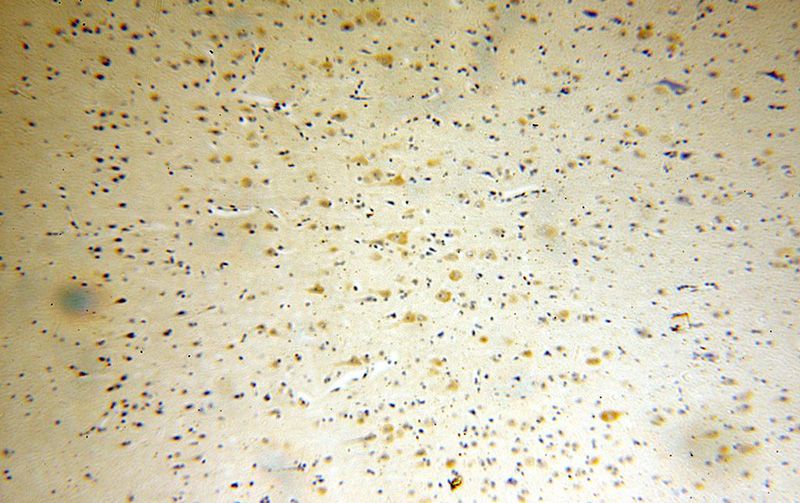
Immunohistochemical of paraffin-embedded human brain using Catalog No:108238(ARC antibody) at dilution of 1:100 (under 10x lens)
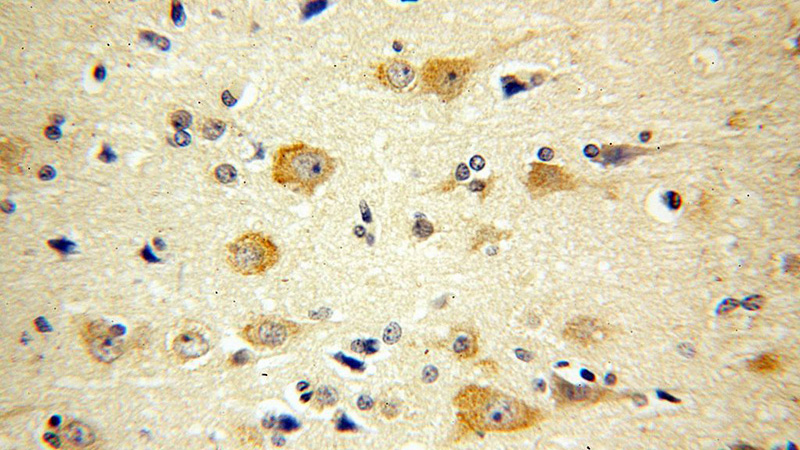
Immunohistochemical of paraffin-embedded human brain using Catalog No:108238(ARC antibody) at dilution of 1:100 (under 40x lens)
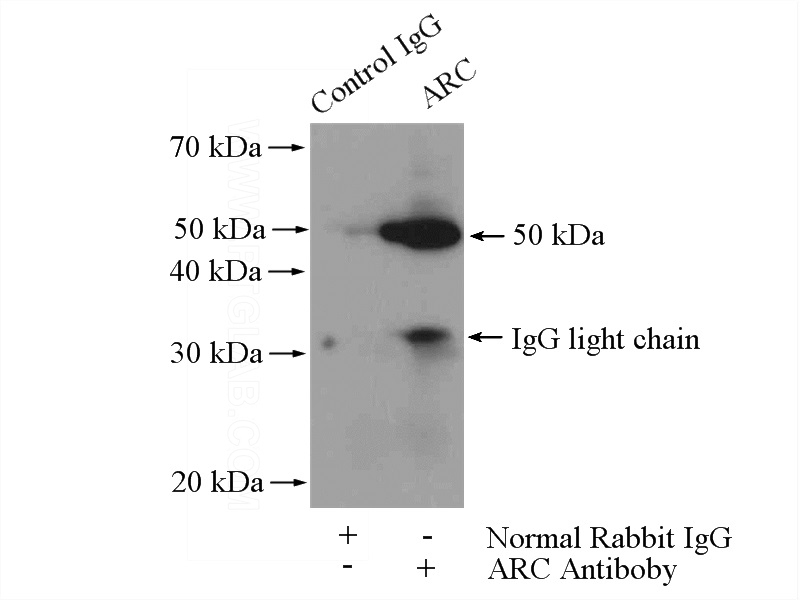
IP Result of anti-ARC (IP:Catalog No:108238, 4ug; Detection:Catalog No:108238 1:300) with mouse brain tissue lysate 4000ug.
-
Background
ARC, also named as KIAA0278 and Arg3.1, mediates endocytosis of neuronal AMPA-type glutamate receptors (AMPARs). It is required for consolidation of synaptic plasticity as well as formation of long-term memory. ARC plays a role in the regulation of cell morphology and cytoskeletal organization. It is required in the stress fiber dynamics and cell migration.
-
References
- Yao J, Chen S, Mao Z, Cadenas E, Brinton RD. 2-Deoxy-D-glucose treatment induces ketogenesis, sustains mitochondrial function, and reduces pathology in female mouse model of Alzheimer's disease. PloS one. 6(7):e21788. 2011.
- Casimiro TM, Nawy S, Carroll RC. Molecular mechanisms underlying activity-dependent AMPA receptor cycling in retinal ganglion cells. Molecular and cellular neurosciences. 56:384-92. 2013.
Related Products / Services
Please note: All products are "FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY AND ARE NOT INTENDED FOR DIAGNOSTIC OR THERAPEUTIC USE"
