-
Product Name
APC antibody
- Documents
-
Description
APC Rabbit Polyclonal antibody. Positive IHC detected in human breast cancer tissue, human colon cancer tissue, human colon tissue, human endometrial cancer tissue.
-
Tested applications
ELISA, IHC
-
Species reactivity
Human,Mouse,Rat; other species not tested.
-
Alternative names
adenomatous polyposis coli antibody; APC antibody; BTPS2 antibody; Deleted in polyposis 2.5 antibody; DP2 antibody; DP2.5 antibody; DP3 antibody; Protein APC antibody
-
Isotype
Rabbit IgG
-
Preparation
This antibody was obtained by immunization of Peptide (Accession Number: NM_000038). Purification method: Antigen affinity purified.
-
Clonality
Polyclonal
-
Formulation
PBS with 0.02% sodium azide and 50% glycerol pH 7.3.
-
Storage instructions
Store at -20℃. DO NOT ALIQUOT
-
Applications
Recommended Dilution:
IHC: 1:20-1:200
-
Validations
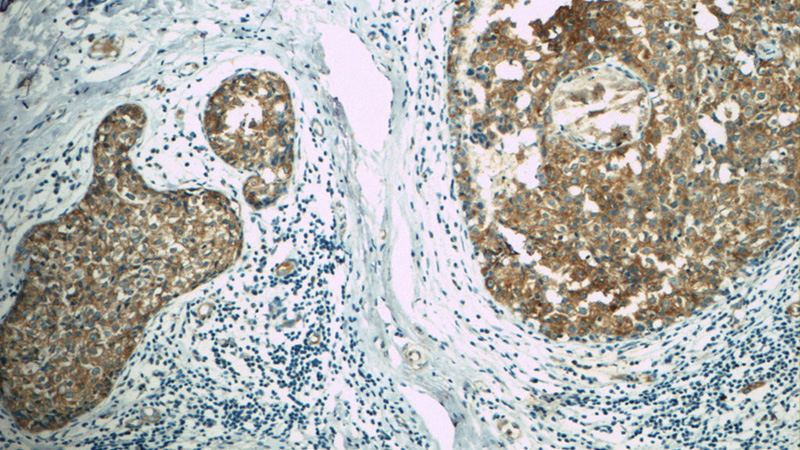
Immunohistochemistry of paraffin-embedded human breast cancer tissue slide using Catalog No:108131(APC Antibody) at dilution of 1:50. Heat mediated antigen retrieved with Citric acid buffer, pH6.0.
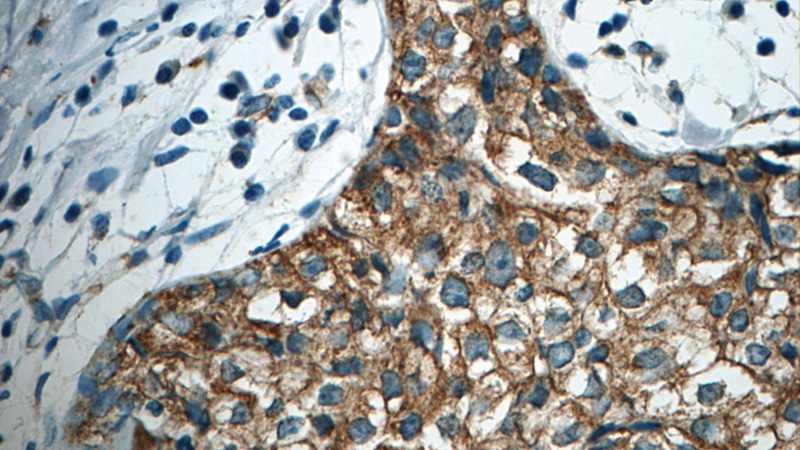
Immunohistochemistry of paraffin-embedded human breast cancer tissue slide using Catalog No:108131 (APC Antibody) at dilution of 1:50. Heat mediated antigen retrieved with Citric acid buffer, pH6.0.
-
Background
APC, also named as DP2.5, belongs to the adenomatous polyposis coli (APC) family. APC is a tumor suppressor that regulates cell division, helps ensure that the number of chromosomes in a cell is correct following cell division, and associates with other proteins involved in cell attachment and signaling. APC promotes rapid degradation of CTNNB1 and participates in Wnt signaling as a negative regulator. It plays a critical role in several cellular processes. APC regulates beta-catenin levels through Wnt-signaling and is involved in actin cytoskeletal integrity, cell-cell adhesion and cell migration. APC activity is correlated with its phosphorylation state. Defects in APC are a cause of familial adenomatous polyposis (FAP) which includes also Gardner syndrome (GS). Defects in APC are a cause of hereditary desmoid disease (HDD) which also known as familial infiltrative fibromatosis (FIF). Defects in APC are a cause of medulloblastoma (MDB) which is a malignant, invasive embryonal tumor of the cerebellum with a preferential manifestation in children. Defects in APC are a cause of mismatch repair cancer syndrome (MMRCS) which also known as Turcot syndrome or brain tumor-polyposis syndrome 1 (BTPS1).
Related Products / Services
Please note: All products are "FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY AND ARE NOT INTENDED FOR DIAGNOSTIC OR THERAPEUTIC USE"
