-
Product Name
Anti-YAP1 Rabbit antibody
- Documents
-
Description
YAP1 Rabbit polyclonal antibody
-
Tested applications
WB, ICC/IF
-
Species reactivity
Human, Mouse
-
Alternative names
YAP; YKI; COB1; YAP2; YAP65 antibody
-
Isotype
Rabbit IgG
-
Preparation
Antigen: A synthetic peptide of human YAP1
-
Clonality
Polyclonal
-
Formulation
Supplied in 50nM Tris-Glycine(pH 7.4), 0.15M Nacl, 40%Glycerol, 0.01% sodium azide and 0.05% BSA.
-
Storage instructions
Store at -20°C. Stable for 12 months from date of receipt.
-
Applications
WB: 1/1000
ICC/IF: 1/100
-
Validations

Western blot detection of YAP1 in Hela cell lysates using YAP1 Rabbit pAb(1:1000 diluted).Predicted band size:55kDa.Observed band size:70-75kDa.
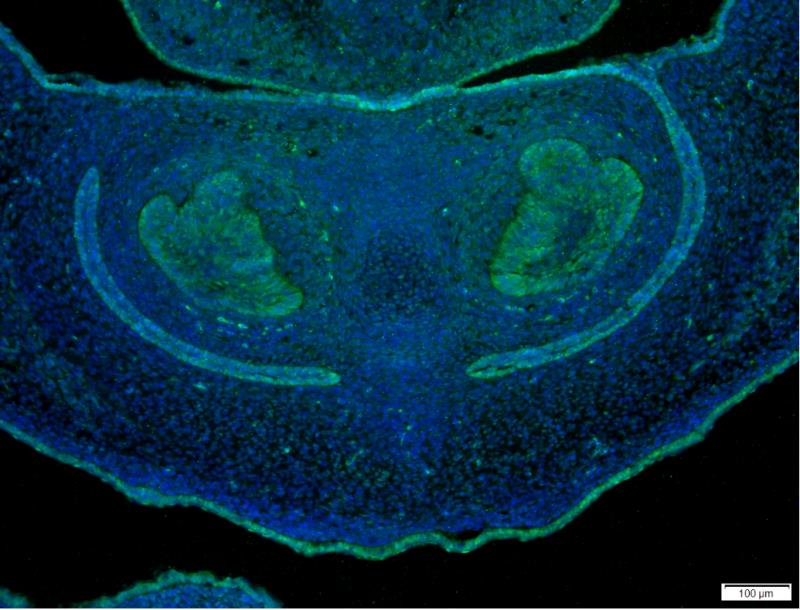
Immunofluorescent analysis of mouse embryo tissue, using YAP1 Antibody .
-
Background
Swiss-Prot Acc.P46937.Transcriptional regulator which can act both as a coactivator and a corepressor and is the critical downstream regulatory target in the Hippo signaling pathway that plays a pivotal role in organ size control and tumor suppression by restricting proliferation and promoting apoptosis (PubMed:17974916, PubMed:18280240, PubMed:18579750, PubMed:21364637). The core of this pathway is composed of a kinase cascade wherein STK3/MST2 and STK4/MST1, in complex with its regulatory protein SAV1, phosphorylates and activates LATS1/2 in complex with its regulatory protein MOB1, which in turn phosphorylates and inactivates YAP1 oncoprotein and WWTR1/TAZ (PubMed:18158288). Plays a key role in tissue tension and 3D tissue shape by regulating cortical actomyosin network formation. Acts via ARHGAP18, a Rho GTPase activating protein that suppresses F-actin polymerization (PubMed:25778702). Plays a key role to control cell proliferation in response to cell contact. Phosphorylation of YAP1 by LATS1/2 inhibits its translocation into the nucleus to regulate cellular genes important for cell proliferation, cell death, and cell migration (PubMed:18158288). The presence of TEAD transcription factors are required for it to stimulate gene expression, cell growth, anchorage-independent growth, and epithelial mesenchymal transition (EMT) induction (PubMed:18579750).
Related Products / Services
Please note: All products are "FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY AND ARE NOT INTENDED FOR DIAGNOSTIC OR THERAPEUTIC USE"
