-
Product Name
Anti-Syntenin (3D9) Mouse antibody
- Documents
-
Description
Syntenin (3D9) Mouse monoclonal antibody
-
Tested applications
WB
-
Species reactivity
Human
-
Alternative names
MDA-9;MDA9;Melanoma differentiation-associated protein 9;Pro-TGF-alpha cytoplasmic domain-interacting protein 18;Scaffold protein Pbp1;SDCB1_HUMAN;Sdcbp;SDCBP;ST1;SYCL; Syndecan binding protein (syntenin);Syndecan binding protein 1;Syndecan-binding protei antibody
-
Isotype
Mouse IgG2b
-
Preparation
Antigen: Purified recombinant human Syntenin protein fragments expressed in E.coli.
-
Clonality
Monoclonal
-
Formulation
Purified mouse monoclonal in buffer containing 0.1M Tris-Glycine (pH 7.4 150 mM NaCl) with 0.02% sodium azide 50% glycerol
-
Storage instructions
Store at 4°C short term. Store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze / thaw cycle.
-
Applications
WB: 1/1000
-
Validations
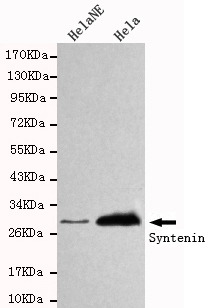
Western blot detection of Syntenin in HelaNE and Hela cell lysates using Syntenin mouse mAb (1:1000 diluted).Predicted band size:32KDa.Observed band size:32KDa.
-
Background
Swiss-Prot Acc.O00560.The protein encoded by this gene was initially identified as a molecule linking syndecan-mediated signaling to the cytoskeleton. The syntenin protein contains tandemly repeated PDZ domains that bind the cytoplasmic, C-terminal domains of a variety of transmembrane proteins. This protein may also affect cytoskeletal-membrane organization, cell adhesion, protein trafficking, and the activation of transcription factors. The protein is primarily localized to membrane-associated adherens junctions and focal adhesions but is also found at the endoplasmic reticulum and nucleus. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants encoding different isoforms. Related pseudogenes have been identified on multiple chromosomes.
Related Products / Services
Please note: All products are "FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY AND ARE NOT INTENDED FOR DIAGNOSTIC OR THERAPEUTIC USE"
