-
Product Name
Monomethylauristatin F (MMAF) Monoclonal Antibody
- Documents
-
Description
Product has been tested in direct ELISA.
-
Tested applications
ELISA
-
Species reactivity
Chemical
-
Isotype
Mouse IgG2b, κ
-
Preparation
MMAF conjugated with BSA. Protein G affinity purified
-
Clonality
Monoclonal
-
Formulation
PBS(pH7.4), lyophilized. Reconstitution: Adding sterile water, prepare a stock solution of 2.0 mg/ml.
-
Storage instructions
Store at -20℃. Avoid freeze / thaw cycles.
-
Applications
ELISA: 1:5,000-1:20,000
-
Validations
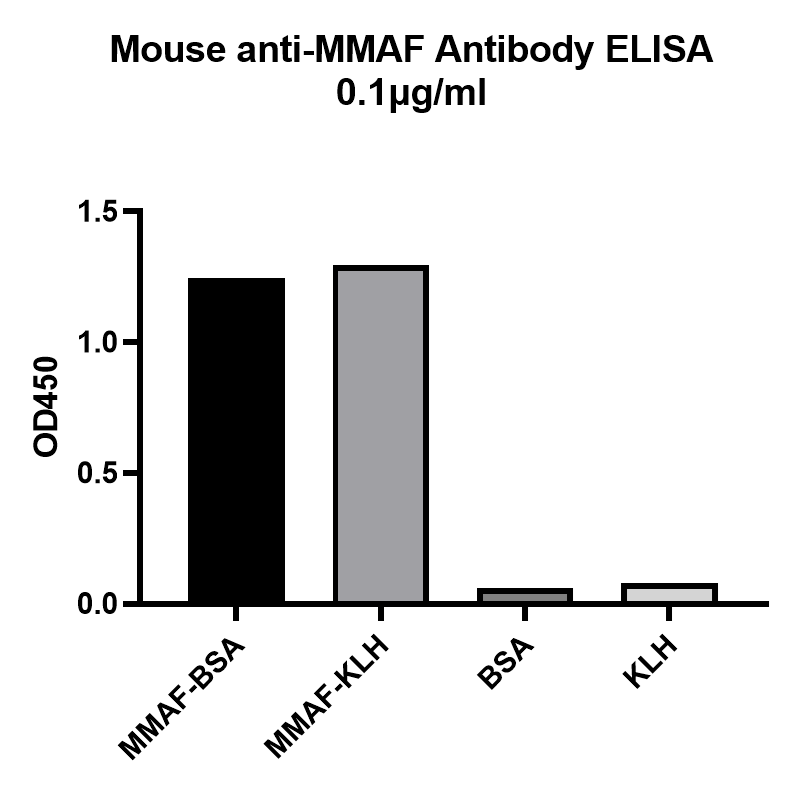
ELISA Binding Assay of Anti-MMAF Antibody to different proteins.
ELISA analysis of Anti-MMAF Monoclonal Antibody with MMAF-BSA, MMAF-KLH, BSA and KLH. Anti-MMAF Monoclonal Antibody can bind to MMAF-BSA or MMAF-KLH, but not carrier proteins.
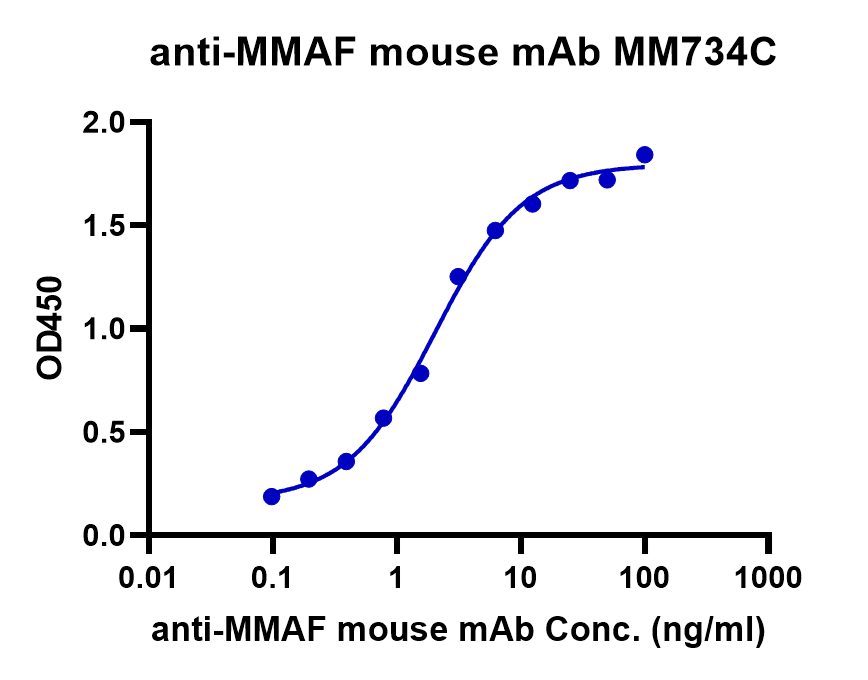
ELISA Binding Assay of Anti-MMAF Antibody
Immobilized MMAF ADC at 2μg/mL (100μL/well) can bind anti-MMAF mouse monoclonal antibody.
-
Background
Auristatins are synthetic analogs of dolastatin 10 (D10), a highly cytotoxic antineoplastic agent employed for cancer chemotherapy, which is derived from a marine species known as Dolabella auricularia. Monomethyl auristatin E (MMAE) and monomethyl auristatin F (MMAF) are identified as the best analogs of dolastatin 10, which bind to microtubules and prevent cell proliferation by inhibiting mitosis. MMAF and MMAE have their advantages and disadvantages. MMAE is more membrane-permeable and has a lower IC50 than MMAF. However, MMAF is more hydrophilic and has a lower aggregation tendency to show lower systemic toxicity than MMAE.
-
References
- Lee JW, Stone RL, Lee SJ, Nam EJ, Roh JW, Nick AM, Han HD, Shahzad MM, Kim HS, Mangala LS, Jennings NB, Mao S, Gooya J, Jackson D, Coleman RL, Sood AK. EphA2 targeted chemotherapy using an antibody drug conjugate in endometrial carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res. 2010 May 1;16(9):2562-70. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-10-0017. Epub 2010 Apr 13. PMID: 20388851; PMCID: PMC3955167.
- Lee JJ, Choi HJ, Yun M, Kang Y, Jung JE, Ryu Y, Kim TY, Cha YJ, Cho HS, Min JJ, Chung CW, Kim HS. Enzymatic prenylation and oxime ligation for the synthesis of stable and homogeneous protein-drug conjugates for targeted therapy. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2015 Oct 5;54(41):12020-4. doi: 10.1002/anie.201505964. Epub 2015 Aug 28. PMID: 26315561.
Related Products / Services
Please note: All products are "FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY AND ARE NOT INTENDED FOR DIAGNOSTIC OR THERAPEUTIC USE"
