-
Product Name
Anti-KRAS antibody
- Documents
-
Description
Rabbit Polyclonal to Human KRAS
-
Tested applications
WB
-
Species reactivity
Human K-Ras
-
Alternative names
Kras-2 antibody; K-RAS2A antibody; K-RAS2B antibody; K-RAS4A antibody; MGC7141 antibody; p21B antibody; ras antibody; AI929937 antibody; C-K-RAS antibody; KI-RAS antibody; Ki-ras antibody; KRAS antibody; Kras antibody; KRAS1 antibody; K-RAS4B antibody; NS antibody; NS3 antibody; RASK2 antibody; RP24-359O2.1 antibody; K-RAS antibody; Kras2 antibody; NS antibody; CFC2 antibody; RALD antibody; ras antibody; Kras2 antibody; K-Ras antibody; KRAS2 antibody; NS3 antibody; CFC2 antibody; KRAS1 antibody; KRAS2 antibody; RASK2 antibody; KI-RAS antibody; C-K-RAS antibody; K-RAS2A antibody; K-RAS2B antibody; K-RAS4A antibody; K-RAS4B antibody; p21B antibody; K-ras antibody; Ki-ras antibody; Kras-2 antibody; AI929937 antibody
-
Isotype
Rabbit IgG
-
Preparation
Produced in rabbits immunized with a synthetic peptide corresponding to the center region of the Human K-Ras, and purified by antigen affinity chromatography.
-
Clonality
Polyclonal
-
Formulation
0.2 μm filtered solution in PBS
-
Storage instructions
This antibody can be stored at 2℃-8℃ for one month without detectable loss of activity. Antibody products are stable for twelve months from date of receipt when stored at -20℃ to -80℃. Preservative-Free.
Sodium azide is recommended to avoid contamination (final concentration 0.05%-0.1%). It is toxic to cells and should be disposed of properly. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles. -
Applications
WB: 5-20 μg/ml
-
Validations
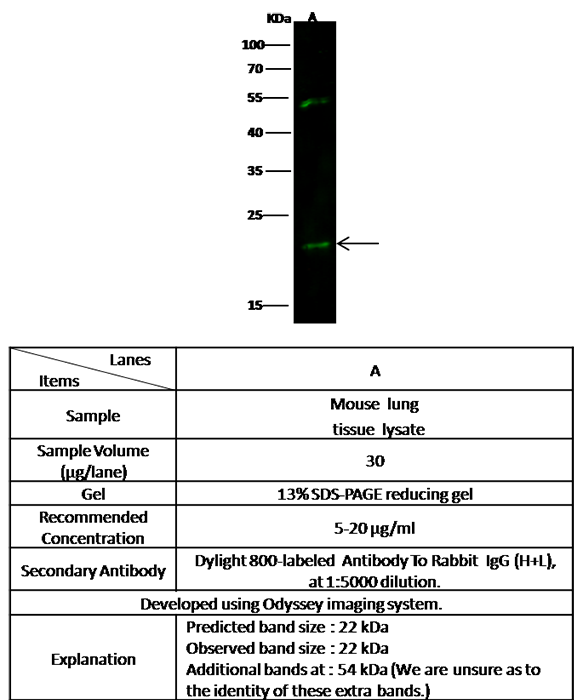
K-Ras Antibody, Rabbit PAb, Antigen Affinity Purified, Western blot
-
Background
K-Ras belongs to the small GTPase superfamily, Ras family. As other members of the Ras family, K-Ras is a GTPase and is an early player in many signal transduction pathways. It is usually tethered to cell membranes because of the presence of an isoprenyl group on its C-terminus. K-Ras functions as a molecular on/off switch. Once it is turned on it recruits and activates proteins necessary for the propagation of growth factor and other receptors' signal, such as c-Raf and PI 3-kinase. It binds to GTP in the active state and possesses an intrinsic enzymatic activity which cleaves the terminal phosphate of the nucleotide converting it to GDP. Upon conversion of GTP to GDP, K-Ras is turned off. The rate of conversion is usually slow but can be sped up dramatically by an accessory protein of the GTPase activating protein class, for example RasGAP. In turn K-Ras can bind to proteins of the Guanine Nucleotide Exchange Factor class, for example SOS1, which forces the release of bound nucleotide. Subsequently, K-Ras binds GTP present in the cytosol and the GEF is released from ras-GTP. Besides essential function in normal tissue signaling, the mutation of a K-Ras gene is an essential step in the development of many cancers. Several germline K-Ras mutations have been found to be associated with Noonan syndrome[4] and cardio-facio-cutaneous syndrome. Somatic K-Ras mutations are found at high rates in Leukemias, colon cancer, pancreatic cancer and lung cancer.Immune Checkpoint Immunotherapy Cancer Immunotherapy Targeted Therapy
Related Products / Services
Please note: All products are "FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY AND ARE NOT INTENDED FOR DIAGNOSTIC OR THERAPEUTIC USE"
