-
Product Name
Anti-GFAP Rabbit antibody
- Documents
-
Description
GFAP Rabbit polyclonal antibody
-
Tested applications
WB, IHC-P, ICC/IF
-
Species reactivity
Human, Rat
-
Isotype
Rabbit IgG
-
Preparation
Antigen: A synthesized peptide derived from human GFAP
-
Clonality
Polyclonal
-
Formulation
Rabbit IgG in phosphate buffered saline , pH 7.4, 150mM NaCl, 0.02% sodium azide and 50% glycerol.
-
Storage instructions
Store at 4°C short term. Store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze / thaw cycle.
-
Applications
WB: 1/500-1/2000
IHC: 1/50-1/200
ICC/IF: 1/50-1/200
-
Validations
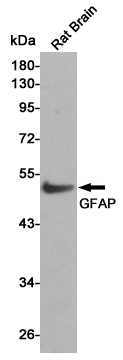
Western blot analysis of GFAP expression in Rat brain lysate.
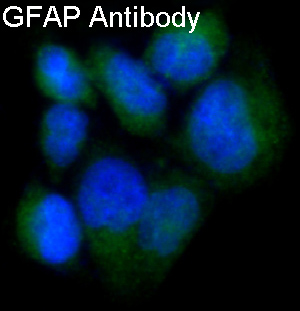
Immunofluorescent analysis of SNB19 cells, using GFAP Antibody.
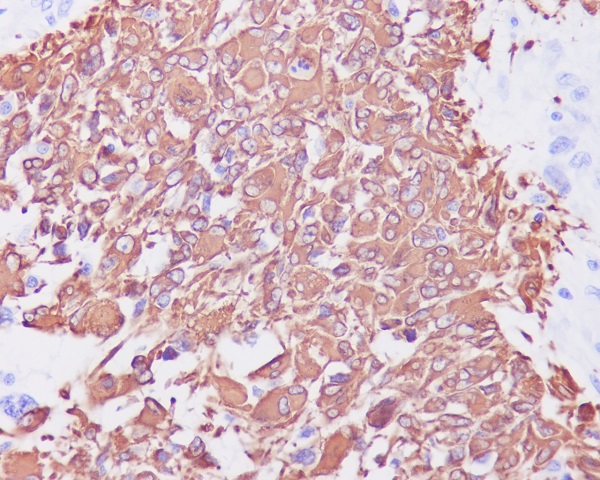
Immunohistochemical analysis of paraffin-embedded human glioma, using GFAP Antibody .
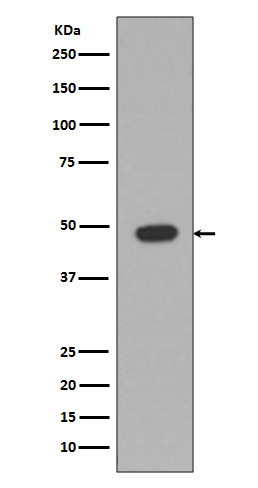
Western blot analysis of GFAP expression in Rat Brain cell lysates using GFAP antibody at 1/1000 dilution.Predicted band size:50KDa.Observed band size:50KDa.
-
Background
Swiss-Prot Acc.P14136.The cytoskeleton consists of three types of cytosolic fibers: microfilaments (actin filaments), intermediate filaments, and microtubules. Major types of intermediate filaments are specifically expressed in particular cell types: cytokeratins in epithelial cells, glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP) in glial cells, desmin in skeletal, visceral, and certain vascular smooth muscle cells, vimentin in cells of mesenchymal origin, and neurofilaments in neurons. GFAP and vimentin form intermediate filaments in astroglial cells and modulate their motility and shape.
-
References
- Effect of photobiomodulation on neural differentiation of human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells
Related Products / Services
Please note: All products are "FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY AND ARE NOT INTENDED FOR DIAGNOSTIC OR THERAPEUTIC USE"
