-
Product Name
Anti- antibody
- Documents
-
Description
Rabbit polyclonal antibody to
-
Tested applications
IF, IHC-P, ELISA
-
Species reactivity
Arabidopsis thaliana
-
Alternative names
F27M3.7 antibody; F27M3_7 antibody
-
Isotype
Rabbit IgG
-
Preparation
This antigen of this antibody was c-terminal a. thaliana ap-4 complex subunit epsilon.
-
Clonality
Polyclonal
-
Formulation
Liquid, 1*PBS (pH7.4), 0.2% BSA, 50% Glycerol. Preservative: 0.05% Sodium Azide.
-
Storage instructions
Store at +4℃ after thawing. Aliquot store at -20℃. Avoid repeated freeze / thaw cycles.
-
Applications
IF:1:50-1:100
IHC-P:1:50-1:200
ELISA:1:10,000-1:20,000
-
Validations
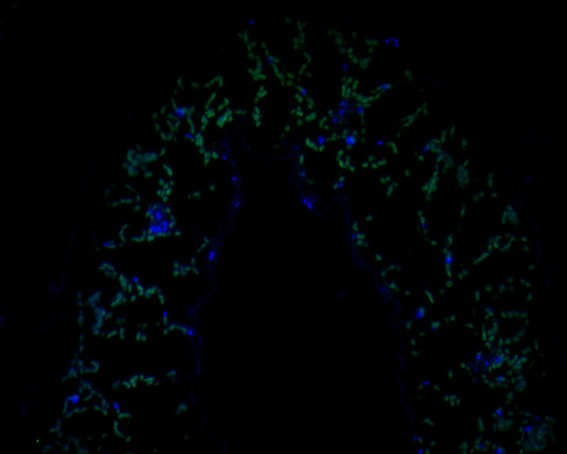
Fig1:; Immunofluorescence staining of paraffin-embedded A. thaliana tissue using anti-AP-4 complex subunit epsilon antibody. The section was pre-treated using heat mediated antigen retrieval with Tris-EDTA buffer (pH 9.0) for 20 minutes. The tissues were blocked in 10% negative goat serum for 1 hour at room temperature, washed with PBS, and then probed with 175163# at 1/50 dilution for 10 hours at 4℃ and detected using Alexa Fluor® 488 conjugate-Goat anti-Rabbit IgG (H+L) Secondary Antibody at a dilution of 1:500 for 1 hour at room temperature.
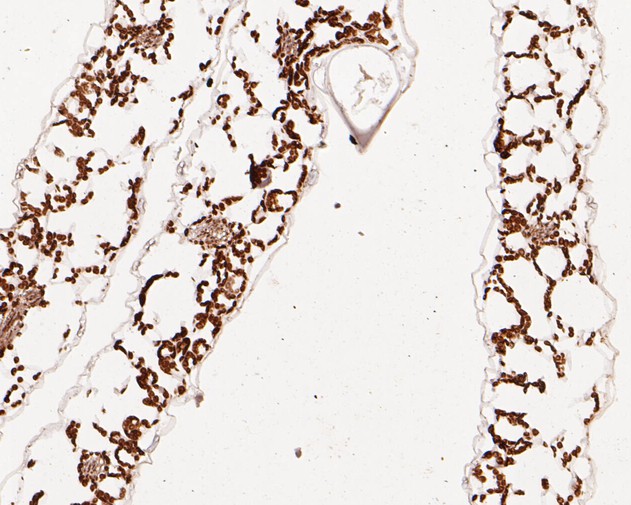
Fig2:; Immunohistochemical analysis of paraffin-embedded A. thaliana tissue using anti-AP-4 complex subunit epsilon antibody. The section was pre-treated using heat mediated antigen retrieval with Tris-EDTA buffer (pH 8.0-8.4) for 20 minutes.The tissues were blocked in 5% BSA for 30 minutes at room temperature, washed with ddH; 2; O and PBS, and then probed with the primary antibody ( 1/50) for 30 minutes at room temperature. The detection was performed using an HRP conjugated compact polymer system. DAB was used as the chromogen. Tissues were counterstained with hematoxylin and mounted with DPX.
- Background
-
References
- Ivankovic D. et. al. Axonal autophagosome maturation defect through failure of ATG9A sorting underpins pathology in AP-4 deficiency syndrome. Autophagy. 2019 May 29:1-17.
- De Pace R. et. al. Altered distribution of ATG9A and accumulation of axonal aggregates in neurons from a mouse model of AP-4 deficiency syndrome.PLoS Genet. 2018 Apr 26;14(4):e1007363.
Related Products / Services
Please note: All products are "FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY AND ARE NOT INTENDED FOR DIAGNOSTIC OR THERAPEUTIC USE"
