-
Product Name
AKT1 antibody
- Documents
-
Description
AKT1 Rabbit Polyclonal antibody. Positive WB detected in multi-cells, COLO 320 cells. Positive IHC detected in human breast cancer tissue, human cervical cancer tissue. Positive IF detected in HeLa cells. Observed molecular weight by Western-blot: 62kd
-
Tested applications
ELISA, IHC, WB, IF
-
Species reactivity
Human; other species not tested.
-
Alternative names
AKT antibody; AKT1 antibody; PKB antibody; PKB ALPHA antibody; PRKBA antibody; Protein kinase B antibody; Proto oncogene c Akt antibody; RAC antibody; RAC ALPHA antibody; RAC PK alpha antibody
-
Isotype
Rabbit IgG
-
Preparation
This antibody was obtained by immunization of Peptide (Accession Number: XM_005267401). Purification method: Antigen affinity purified.
-
Clonality
Polyclonal
-
Formulation
PBS with 0.02% sodium azide and 50% glycerol pH 7.3.
-
Storage instructions
Store at -20℃. DO NOT ALIQUOT
-
Applications
Recommended Dilution:
WB: 1:200-1:2000
IHC: 1:20-1:200
IF: 1:10-1:100
-
Validations
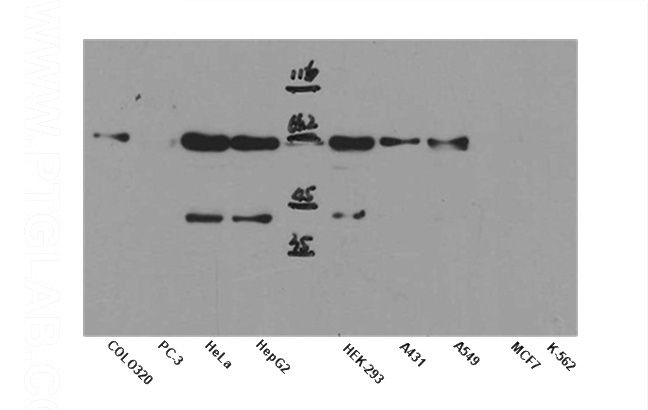
WB result of anti-AKT1 (Catalog No:107947) in different cell lysates.
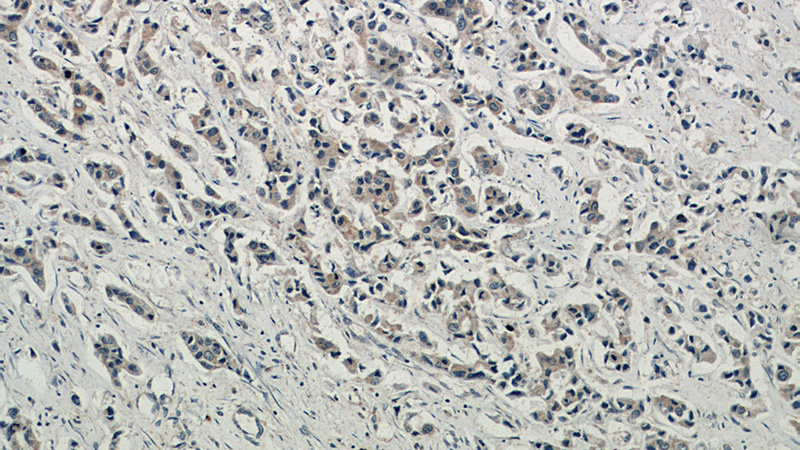
Immunohistochemical of paraffin-embedded human breast cancer using Catalog No:107947(AKT1 antibody) at dilution of 1:50 (under 10x lens)
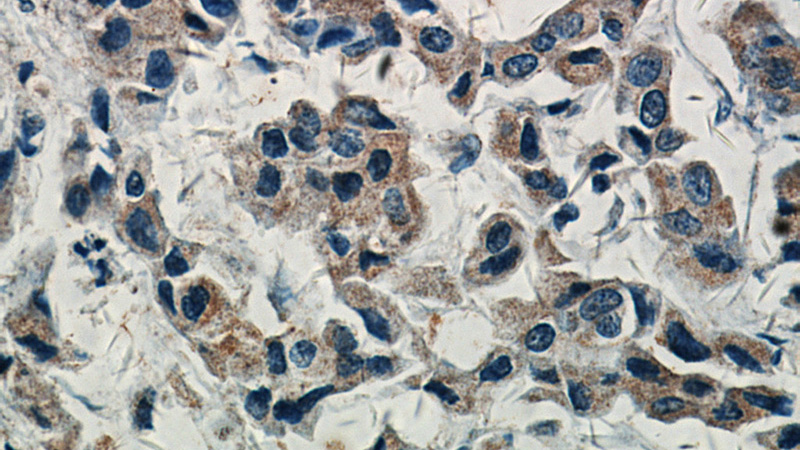
Immunohistochemical of paraffin-embedded human breast cancer using Catalog No:107947(AKT1 antibody) at dilution of 1:50 (under 40x lens)
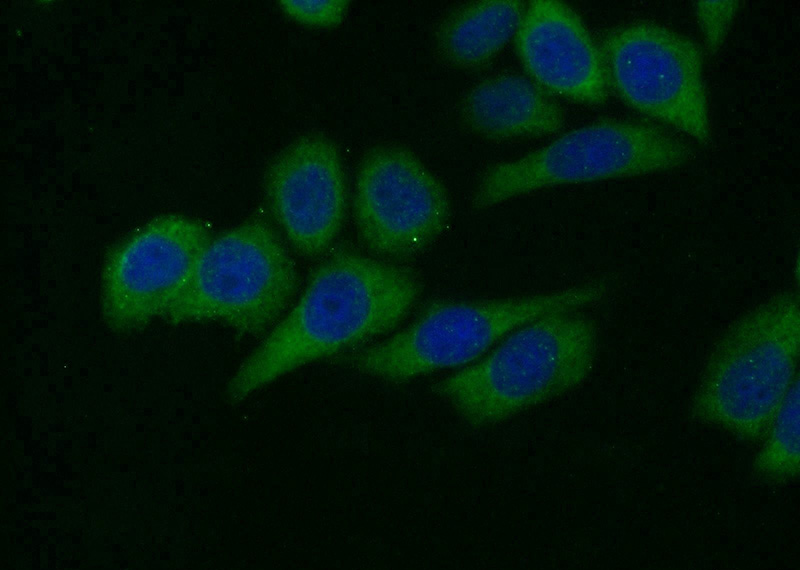
Immunofluorescent analysis of HeLa cells using Catalog No:107947(AKT1 Antibody) at dilution of 1:25 and Alexa Fluor 488-congugated AffiniPure Goat Anti-Rabbit IgG(H+L)
-
Background
The serine-threonine protein kinase AKT1 is catalytically inactive in serum-starved primary and immortalized fibroblasts. AKT1 and the related AKT2 are activated by platelet-derived growth factor. The activation is rapid and specific, and it is abrogated by mutations in the pleckstrin homology domain of AKT1. It was shown that the activation occurs through phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase. In the developing nervous system AKT is a critical mediator of growth factor-induced neuronal survival. Survival factors can suppress apoptosis in a transcription-independent manner by activating the serine/threonine kinase AKT1, which then phosphorylates and inactivates components of the apoptotic machinery.
Related Products / Services
Please note: All products are "FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY AND ARE NOT INTENDED FOR DIAGNOSTIC OR THERAPEUTIC USE"
