-
Product Name
SMCHD1 Polyclonal Antibody
- Documents
-
Description
Polyclonal antibody to SMCHD1
-
Tested applications
WB, IF
-
Species reactivity
Human, Mouse, Rat
-
Alternative names
SMCHD1 antibody; BAMS antibody; FSHD2 antibody; structural maintenance of chromosomes flexible hinge domain containing 1 antibody
-
Isotype
Rabbit IgG
-
Preparation
Antigen: Recombinant fusion protein containing a sequence corresponding to amino acids 1756-2005 of human SMCHD1 (NP_056110.2).
-
Clonality
Polyclonal
-
Formulation
PBS with 0.02% sodium azide, 50% glycerol, pH7.3.
-
Storage instructions
Store at -20℃. Avoid freeze / thaw cycles.
-
Applications
WB 1:500 - 1:2000
IF 1:50 - 1:100 -
Validations
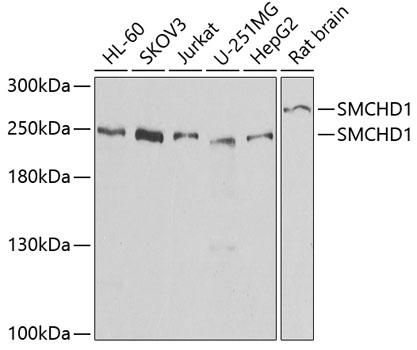
Western blot - SMCHD1 Polyclonal Antibody
Western blot analysis of extracts of various cell lines, using SMCHD1 antibody at 1:1000 dilution.Secondary antibody: HRP Goat Anti-Rabbit IgG (H+L) at 1:10000 dilution.Lysates/proteins: 25ug per lane.Blocking buffer: 3% nonfat dry milk in TBST.Detection: ECL Basic Kit .Exposure time: 30s.
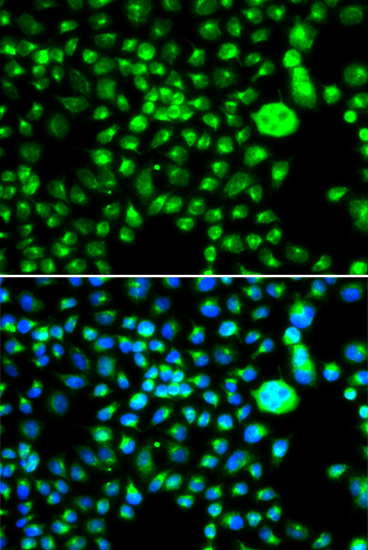
Immunofluorescence - SMCHD1 Polyclonal Antibody
Immunofluorescence analysis of MCF-7 cells using SMCHD1 antibody . Blue: DAPI for nuclear staining.
-
Background
Non-canonical member of the structural maintenance of chromosomes (SMC) protein family that plays a key role in epigenetic silencing by regulating chromatin architecture (By similarity). Promotes heterochromatin formation in both autosomes and chromosome X, probably by mediating the merge of chromatin compartments (By similarity). Plays a key role in chromosome X inactivation in females by promoting the spreading of heterochromatin. Recruited to inactivated chromosome X by Xist RNA and acts by mediating the merge of chromatin compartments: promotes random chromatin interactions that span the boundaries of existing structures, leading to create a compartment-less architecture typical of inactivated chromosome X (By similarity). Required to facilitate Xist RNA spreading (By similarity). Also required for silencing of a subset of clustered autosomal loci in somatic cells, such as the DUX4 locus. Has ATPase activity; may participate in structural manipulation of chromatin in an ATP-dependent manner as part of its role in gene expression regulation. Also plays a role in DNA repair: localizes to sites of DNA double-strand breaks in response to DNA damage to promote the repair of DNA double-strand breaks. Acts by promoting non-homologous end joining (NHEJ) and inhibiting homologous recombination (HR) repair.
Related Products / Services
Please note: All products are "FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY AND ARE NOT INTENDED FOR DIAGNOSTIC OR THERAPEUTIC USE"
