-
Product Name
Mouse SIRPB1A (His Tag) recombinant protein
- Documents
-
Description
SIRPB1A (Signal-regulatory protein beta 1A), also known as SIRP beta 1, belongs to signal-regulatory-protein (SIRP) family, and immunoglobulin superfamily. Signal-regulatory proteins (SIRPs) are cell-surface glycoproteins expressed on myeloid and neural cells that have been shown to recruit SH2 domain-containing protein phosphatase 1 (SHP-1) and SHP-2 and to regulate receptor tyrosine kinase-coupled signaling. SIRP are classified as SIRP alpha molecules, containing a 110- to 113-amino acid long, or SIRP beta molecules, with a 5-amino acid long intracytoplasmic domain. SIRP beta 1 is a new DAP12-associated receptor involved in the activation of myeloid cells, which contains a short cytoplasmic domain that lacks sequence motifs capable of recruiting SHP-1 and SHP-2. SIRP beta 1. SIRP beta 1 acts as an activating isoform of SIRP alpha molecules, confirming the co-existence of inhibitory ITIM-bearing molecules, recruiting SHP-1 and SHP-2 protein tyrosine phosphatases, and activating counterparts, whose engagement couples to protein tyrosine kinases via ITAM-bearing molecules.
-
Protein name
SIRP-beta B-type
-
Protein short names
SIRPB1A; SIRP-BETA; 9930027N05RIK; SIRPB; SIRPB1
-
Uniprot ID
Q6F5F0
-
Gene Name
SIRP-beta
-
Source/Expression Host
Human Cells
-
Expression Plasmid/cDNA
A DNA sequence encoding the mouse SIRPB1A (BAD26610.1) (Met 1-Lys 363) was expressed, with a C-terminal polyhistidine tag.
-
Protein Species
Mouse
-
Molecular weight
The secreted recombinant mouse SIRPB1A comprises 348 amino acids and has a calculated molecular mass of 39.1 kDa. As a result of glycosylation, the apparent molecular mass of the recombinant protein is approximately 55-60 kDa in SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions.
-
Purity
> 98 % as determined by SDS-PAGE
-
Validations
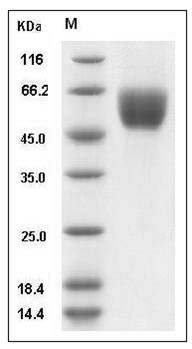
Mouse SIRPB1A / SIRP beta 1 Protein (His Tag) SDS-PAGE
Related Products / Services
Please note: All products are "FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY AND ARE NOT INTENDED FOR DIAGNOSTIC OR THERAPEUTIC USE"
