-
Product Name
Schistosoma japonicum GST 26/SjGST recombinant protein
- Documents
-
Description
Glutathione S-transferases (GSTs), previously known as ligandins, comprise a family of eukaryotic and prokaryotic phase II metabolic isozymes best known for their ability to catalyze the conjugation of the reduced form of glutathione (GSH) to xenobiotic substrates for the purpose of detoxification. The GST family consists of three superfamilies: the cytosolic, mitochondrial, and microsomal (MAPEG) proteins. GST isoenzymes appear to play a central role in the parasite detoxification system. Other functions are also suspected including a role in increasing the solubility of haematin in the parasite gut. The activity of GSTs is dependent upon a steady supply of GSH from the synthetic enzymes gamma-glutamylcysteine synthetase and glutathione synthetase, as well as the action of specific transporters to remove conjugates of GSH from the cell. The primary role of GSTs is to detoxify xenobiotics by catalyzing the nucleophilic attack by GSH on electrophilic carbon, sulfur, or nitrogen atoms of said nonpolar xenobiotic substrates, thereby preventing their interaction with crucial cellular proteins and nucleic acids.
-
Protein name
Glutathione S-transferase class-mu 26 kDa isozyme
-
Protein short names
SjGST
-
Uniprot ID
P08515
-
Source/Expression Host
E. coli
-
Expression Plasmid/cDNA
A DNA sequence encoding the Schistosoma japonicum GST 26/SjGST Met1-Lys218 is expressed.
-
Protein Species
Schistosoma japonicum
-
Purity
>95% as determined by SDS-PAGE.
-
Validations
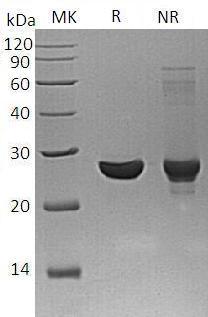
Schistosoma japonicum GST 26/SjGST recombinant protein
Related Products / Services
Please note: All products are "FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY AND ARE NOT INTENDED FOR DIAGNOSTIC OR THERAPEUTIC USE"
