-
Product Name
Rhesus IL-17R/IL-17RA ?CD217? (Fc Tag) recombinant protein
- Documents
-
Description
Interleukin-17 receptor (IL-17R), also known as Interleukin-17 receptor A (IL-17RA) and CD217 antigen (CD217), is a cytokine receptor which binds interleukin 17. IL-17R/IL-17RA (CD217) is a proinflammatory cytokine secreted by activated T-lymphocytes. It is a potent inducer of the maturation of CD34-positive hematopoietic precursors into neutrophils. IL-17R/IL-17RA (CD217) is a ubiquitous type I membrane glycoprotein that binds with low affinity to interleukin 17A. Interleukin 17A and its receptor IL-17RA play a pathogenic role in many inflammatory and autoimmune diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis. Like other cytokine receptors, this receptor likely has a multimeric structure. Defects in IL-17R/IL-17RA (CD217) are the cause of familial candidiasis type 5 (CANDF5). CANDF5 is a rare disorder with altered immune responses and impaired clearance of fungal infections, selective against Candida. It is characterized by persistent and/or recurrent infections of the skin, nails and mucous membranes caused by organisms of the genus Candida, mainly Candida albicans.
-
Protein short names
AW538159; IL-17RA; IL-17R; HIL-17R; CDW217; IL17R; CD217; CANDF5; IL17RA; VDW217; MGC10262
-
Uniprot ID
F6S2R4
-
Source/Expression Host
Human Cells
-
Expression Plasmid/cDNA
A DNA sequence encoding the rhesus IL17RA (XP_001102483.1) (Met1-Trp320) was expressed, fused with the Fc region of human IgG1 at the C-terminus.
-
Protein Species
Rhesus
-
Molecular weight
The recombinant rhesus IL17RA comprises 529 amino acids and has a calculated molecular mass of 60.3 KDa.
-
Purity
> 90 % as determined by SDS-PAGE
-
Activity
Immobilized human IL17A (Cat:503644) at 10 μg/ml (100 μl/well) can bind Rhesus IL17RA-Fc, The EC50 of Rhesus IL17RA-Fc is 0.19-0.43 μg/ml.
-
Validations
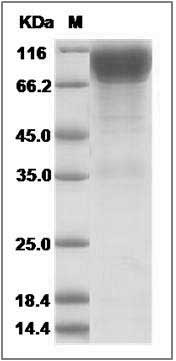
Cynomolgus IL17RA / IL17R Protein (Fc Tag) SDS-PAGE
Related Products / Services
Please note: All products are "FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY AND ARE NOT INTENDED FOR DIAGNOSTIC OR THERAPEUTIC USE"
