-
Product Name
PTTG1 Polyclonal Antibody
- Documents
-
Description
Polyclonal antibody to PTTG1
-
Tested applications
WB, IHC
-
Species reactivity
Human, Mouse, Rat
-
Alternative names
PTTG1 antibody; EAP1 antibody; HPTTG antibody; PTTG antibody; TUTR1 antibody; securin antibody
-
Isotype
Rabbit IgG
-
Preparation
Antigen: Recombinant fusion protein containing a sequence corresponding to amino acids 1-202 of human PTTG1 (NP_001269311.1).
-
Clonality
Polyclonal
-
Formulation
PBS with 0.02% sodium azide, 50% glycerol, pH7.3.
-
Storage instructions
Store at -20℃. Avoid freeze / thaw cycles.
-
Applications
WB 1:500 - 1:2000
IHC 1:100 - 1:200 -
Validations
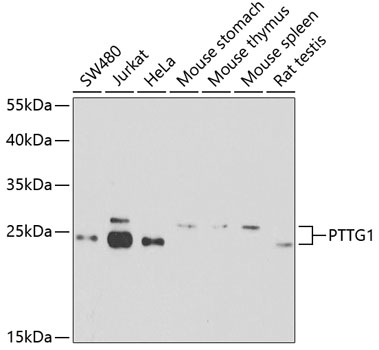
Western blot - PTTG1 Polyclonal Antibody
Western blot analysis of extracts of various cell lines, using PTTG1 antibody at 1:1000 dilution.Secondary antibody: HRP Goat Anti-Rabbit IgG (H+L) at 1:10000 dilution.Lysates/proteins: 25ug per lane.Blocking buffer: 3% nonfat dry milk in TBST.Detection: ECL Basic Kit .Exposure time: 90s.
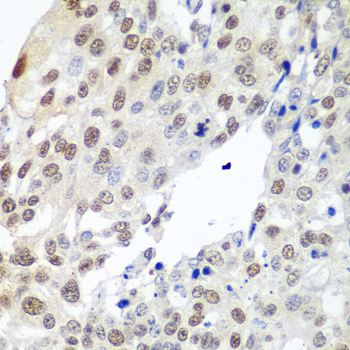
Immunohistochemistry - PTTG1 Polyclonal Antibody
Immunohistochemistry of paraffin-embedded human lung cancer using PTTG1 antibody at dilution of 1:100 (40x lens).
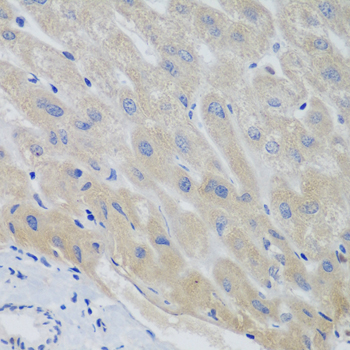
Immunohistochemistry - PTTG1 Polyclonal Antibody
Immunohistochemistry of paraffin-embedded human liver using PTTG1 antibody at dilution of 1:100 (40x lens).
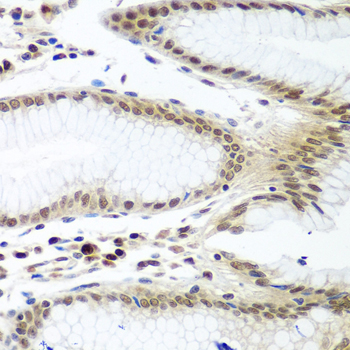
Immunohistochemistry - PTTG1 Polyclonal Antibody
Immunohistochemistry of paraffin-embedded human stomach using PTTG1 antibody at dilution of 1:100 (40x lens).
-
Background
Regulatory protein, which plays a central role in chromosome stability, in the p53/TP53 pathway, and DNA repair. Probably acts by blocking the action of key proteins. During the mitosis, it blocks Separase/ESPL1 function, preventing the proteolysis of the cohesin complex and the subsequent segregation of the chromosomes. At the onset of anaphase, it is ubiquitinated, conducting to its destruction and to the liberation of ESPL1. Its function is however not limited to a blocking activity, since it is required to activate ESPL1. Negatively regulates the transcriptional activity and related apoptosis activity of TP53. The negative regulation of TP53 may explain the strong transforming capability of the protein when it is overexpressed. May also play a role in DNA repair via its interaction with Ku, possibly by connecting DNA damage-response pathways with sister chromatid separation.
Related Products / Services
Please note: All products are "FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY AND ARE NOT INTENDED FOR DIAGNOSTIC OR THERAPEUTIC USE"
