-
Product Name
Mouse ASAH2 (His Tag) recombinant protein
- Documents
-
Description
ASAH2 (N-acylsphingosine amidohydrolase 2), also known as neutral ceramidase, is a type II integral membrane protein that can be cleaved to produce a soluble secreted protein. The enzyme is abundant in the brush border membranes of the intestine, and also expressed in several tissues such as kidney, brain and liver. The primary structure of ASAH2/neutral ceramidase is highly conserved from bacteria to humans, however, there is a clear difference in the molecular architecture. The murine ASAH2 possesses ‘amucin box’, a Ser/Thr/Pro-rich domain glycosylated with O-glycans which is necessary to retain the enzyme on the plasma membrane as a type II integral protein. The major physiological function of ASAH2/neutral ceramidase is the metabolism of dietary sphingolipids, and thus plays a role in the generation of messenger molecules such as sphingosine and sphingosine 1-phosphate.
-
Protein name
N-acylsphingosine amidohydrolase 2
-
Protein short names
BCDASE; N-CDASE; AI585898; NCDASE; HNAC1; LCDASE; ASAH2; MGC129777
-
Uniprot ID
Q9JHE3
-
Gene Name
Asah2; mCG_13039
-
Source/Expression Host
Human Cells
-
Expression Plasmid/cDNA
A DNA sequence encoding the Lumenal domain (Thr 34-Thr 756) of mouse ASAH2 (NP_061300.1) precursor was expressed with a N-terminal polyhistidine tag.
-
Protein Species
Mouse
-
Molecular weight
The secreted recombinant mouse ASAH2 consists of 739 amino acids and has a calculated molecular mass of 82 kDa. As a result of glycosylation, the recombinant protein migrates as an approximately 105-115 kDa protein in SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions.
-
Purity
> 97 % as determined by SDS-PAGE
-
Activity
Measured by its ability to hydrolyze the substrate C12:0 ceramide into sphingosine and dodecanoic acid.
The specific activity is > 3,000 pmoles/min/μg. -
Validations
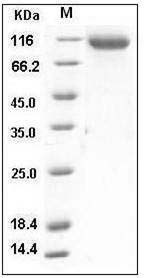
Mouse ASAH2 Protein (His Tag) SDS-PAGE
Related Products / Services
Please note: All products are "FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY AND ARE NOT INTENDED FOR DIAGNOSTIC OR THERAPEUTIC USE"
